Copyright
©The Author(s) 2000.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2000; 6(2): 157-168
Published online Apr 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.157
Published online Apr 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.157
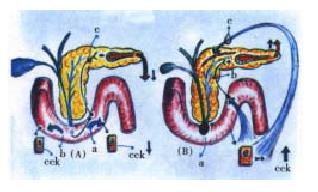
Figure 6 Disruption of the entero-pancreatic feedback loop.
A: Normal condition: Brake of CCK release. Direct brake (trypsin, chymotripsin) of the CCK-releasing peptide and of the monitor peptide (a). Indirect brake (bilis). Stabilization of trypsin and chymot rypsin (b). Bile-pancreatic secretion activation of a negative duodeno-pancre atic reflex (c). B: Bile-pancreatic duct obstruction condition-Loss of the normal bile-pancreatic secretion-evoked brake of CCK release. Stone impactation in the Vaterian papilla (a). CCK-induced paracrine-neural duode no-pancreatic reflex (b). CCK-elicited hormonal activation of pancreon units (c). Neural (b) and hormonal (c) mechanisms. Neural (b) and hormonal (c) pathway to the CCK-evoked supramaximal stimulation of the acinar component of the panc reon units.
- Citation: Tiscornia OM, Hamamura S, Lehmann ES, Otero G, Waisman H, Tiscornia-Wasserman P, Bank S. Biliary acute pancreatitis: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2000; 6(2): 157-168
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v6/i2/157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v6.i2.157