Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2025; 31(9): 98027
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.98027
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.98027
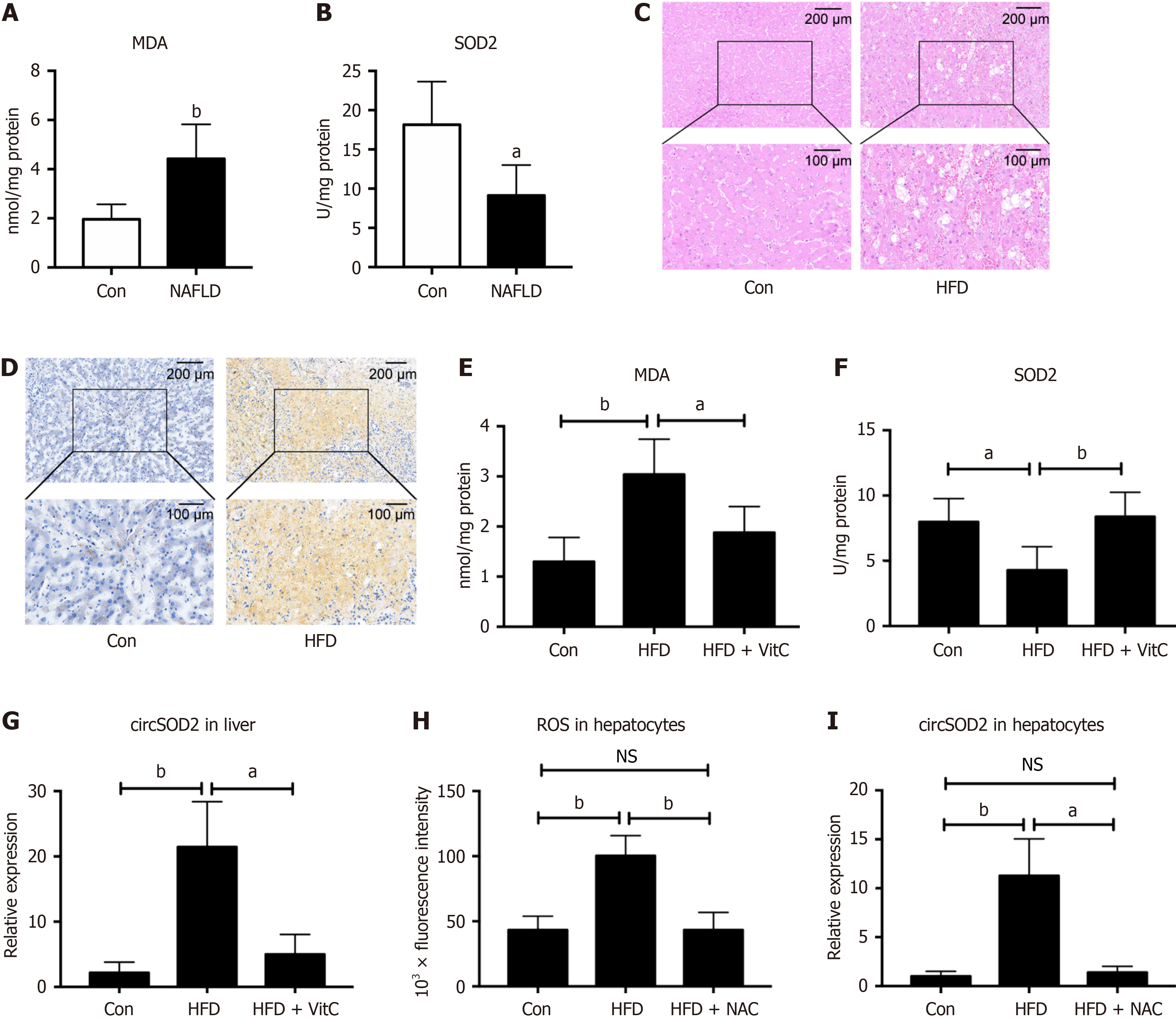
Figure 2 circSOD2 is induced by oxidative stress.
A and B: Levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a lipid peroxidation metabolite, and antioxidant SOD2 in livers of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and control subjects (n = 5); C and D: Representative hematoxylin & eosin and Oil red O staining images confirm the successful establishment of a high-fat diet (HFD) mice model to simulate MAFLD; normal diet mice served as negative control (Con); E-G: MDA, SOD2, and circSOD2 Levels in the livers of Con, HFD, and HFD supplemented with Vitamin C groups (n = 5); H and I: Reactive oxygen species and circSOD2 Levels in primary hepatocytes from Con, HFD, and HFD were pretreated with N-acetyl L-cysteine groups (n = 5). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; NS: Not significant; Con: Control; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; MDA: Malondialdehyde; HFD: High-fat diet; VitC: Vitamin C; NAC: N-acetyl L-cysteine.
- Citation: Li LP, Chen XY, Liu HB, Zhu Y, Xie MJ, Li YJ, Luo M, Albahde M, Zhang HY, Lou JY. Oxidative stress-induced circSOD2 inhibits osteogenesis through sponging miR-29b in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(9): 98027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i9/98027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.98027