Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2025; 31(9): 101383
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.101383
Published online Mar 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.101383
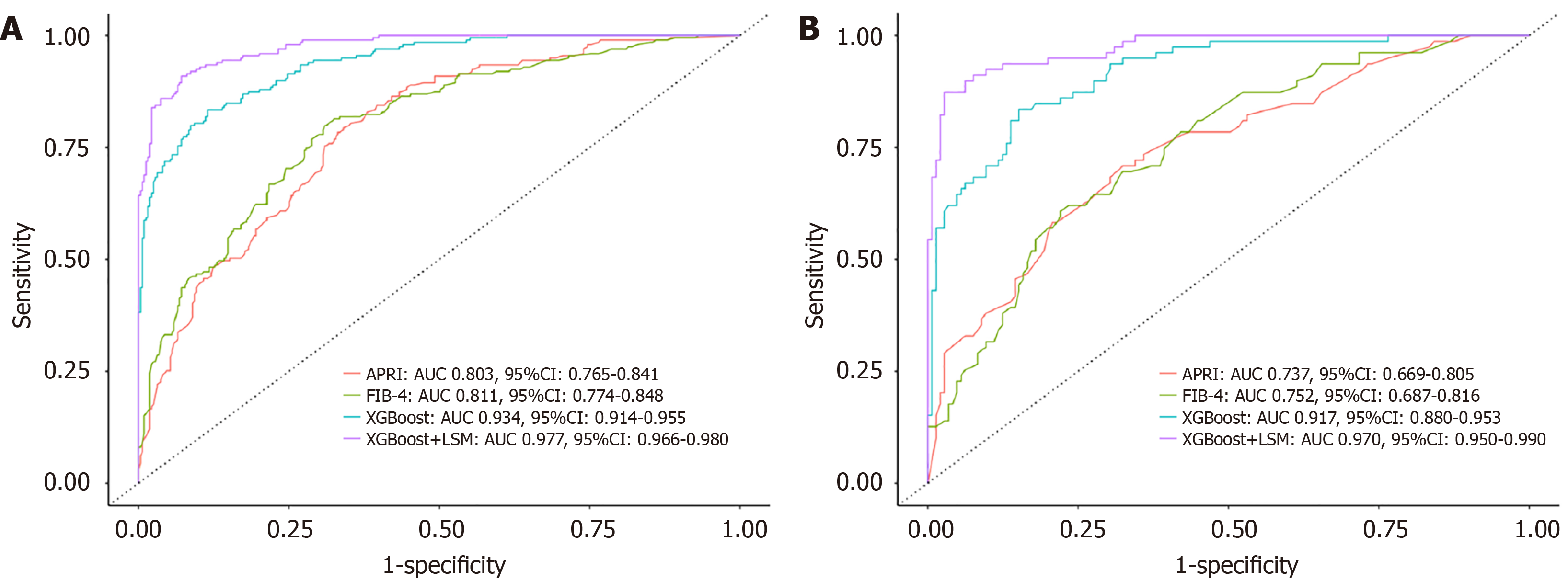
Figure 4 The receiver operating characteristic of comparing Extreme Gradient Boosting models with another non-invasive diagnosis model.
A: Training cohort; B Validation cohort. The receiver operating characteristic of the Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model and XGBoost + liver stiffness measure model were much better than aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index scores and Fibrosis-4 scores. APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index score; FIB-4: Fibrosis index based on the 4 factors; LSM: Liver stiffness measure; AUC: Area under the curve; XGBoost: Extreme Gradient Boosting.
- Citation: Xiong FX, Sun L, Zhang XJ, Chen JL, Zhou Y, Ji XM, Meng PP, Wu T, Wang XB, Hou YX. Machine learning-based models for advanced fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients: A cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(9): 101383
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i9/101383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.101383