Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2025; 31(8): 99036
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.99036
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.99036
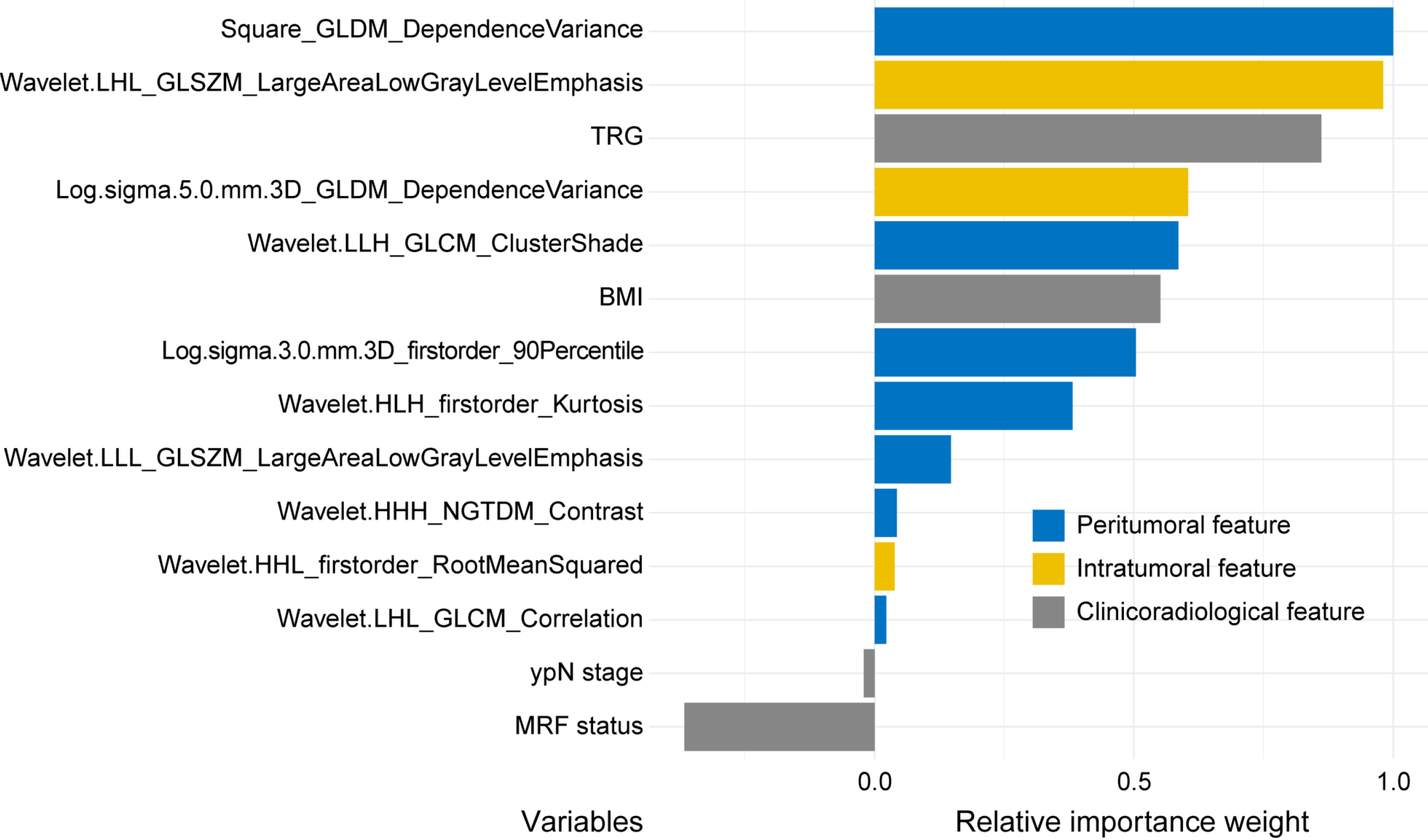
Figure 5 Relative importance weight of variables in integrated clinical-radiological-omics model.
The relative importance weight of a variable was calculated using the permutation feature importance by measuring the change in the model’s C-index after random shuffling of each feature value, with the importance scaled relative to the maximum observed change. BMI: Body mass index; GLCM: Grey level co-occurrence matrix; GLDM: Grey level dependence matrix; GLSZM: Grey level size zone matrix; HHH: High-high-high; HHL: High-high-low; HLH: High-low-high; LHL: Low-high-low; LLH: Low-low-high; LLL: Low-low-low; MRF: Mesorectal fascia; NGTDM: Neighboring grey tone difference matrix; TRG: Tumor regression grade; ypN stage: Pathological N stage after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
- Citation: Liang ZY, Yu ML, Yang H, Li HJ, Xie H, Cui CY, Zhang WJ, Luo C, Cai PQ, Lin XF, Liu KF, Xiong L, Liu LZ, Chen BY. Beyond the tumor region: Peritumoral radiomics enhances prognostic accuracy in locally advanced rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(8): 99036
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i8/99036.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.99036