Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2025; 31(8): 101585
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.101585
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.101585
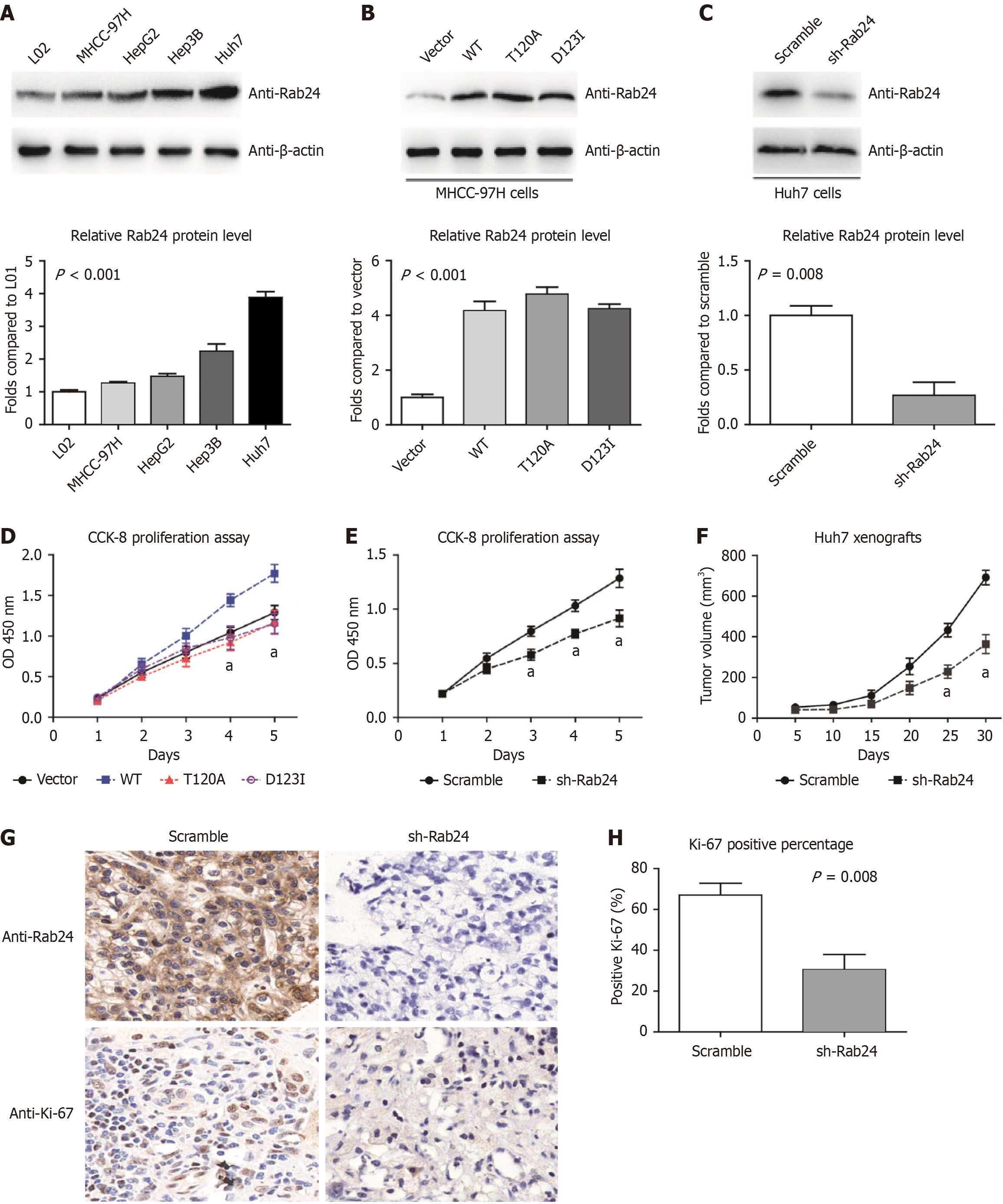
Figure 5 In vitro and in vivo evaluation of Rab24 function in hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
A: Western blotting data demonstrated higher Rab24 protein levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines (Huh7, HepG2, Hep3B, and MHCC-97H) compared to noncancerous hepatocytes (L02); B: MHCC-97H cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-vector, pcDNA3.1-Rab24-WT, pcDNA3.1-Rab24-T120A, or pcDNA3.1-Rab24-d123I plasmids for overexpression experiments; C: Knockdown assay was conducted by transfecting lentivirus shRNA targeting Rab24 in Huh7 cells, using scramble shRNA as control; D: Overexpressing Rab24-WT can significantly enhance the proliferation capacity of MHCC-97H cells, while its T120A or D123I mutants showed no significant difference compared to the control group transfected with pcDNA3.1-vector; E: Silencing Rab24 resulted in a significant inhibition on the proliferation process of Huh7 cells, as revealed by cell counting kit-8 assays; F: Huh7 cells transfected with Rab24-shRNA or scramble shRNA were subcutaneously injected into nude mice for xenograft assays. The tumor growth curve revealed that Rab24-knockdown significantly attenuated HCC growth in vivo; G: The isolated xenografts were tested by immunohistochemistry targeting Rab24 and Ki-67, respectively; H: Statistical analysis of Ki-67 immunoreactivity showed a significant lower Ki-67 Level in xenografts with Rab24-knockdown. Data was shown as mean ± SD and analyze by Student’s t-test. aP < 0.05; CCK-8: Cell counting kit-8; WT: Wild type.
- Citation: Ding H, Ding ZG, Liu S, Mao XN, Lu XS. Ras-related protein Rab24 plays a predictive role in hepatocellular carcinoma and enhanced tumor proliferation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(8): 101585
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i8/101585.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.101585