Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2025; 31(8): 100227
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100227
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100227
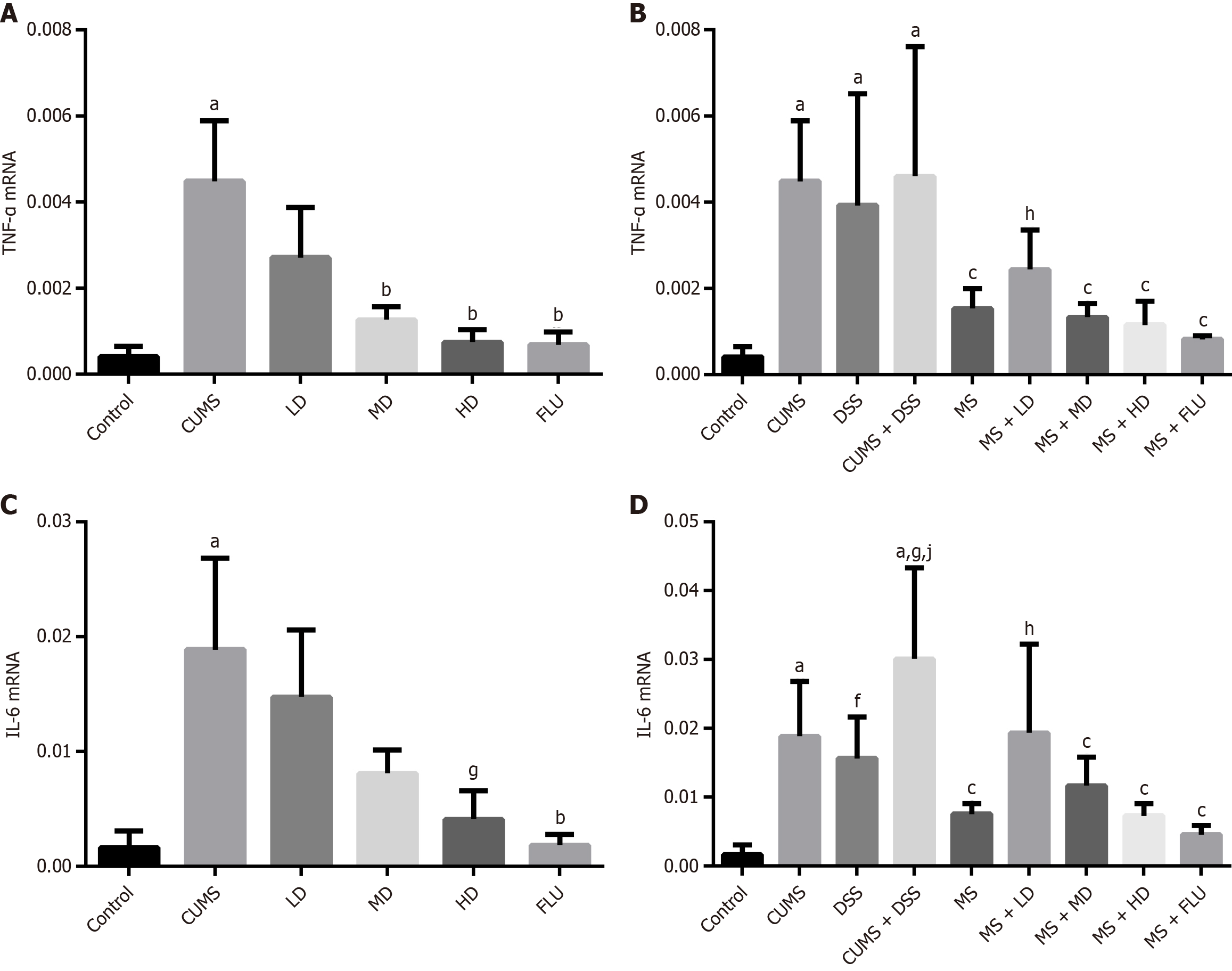
Figure 7 Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 mRNA in colonic tissue after treatment.
A: Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in depression groups; B: Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in chronic restraint stress, dextran sodium sulfate and compound model groups; C: Expression of interleukin-6 mRNA in depression groups; D: Expression of interleukin-6 mRNA in chronic restraint stress, dextran sodium sulfate and compound model groups. aP < 0.01 vs control group; bP < 0.01 vs chronic restraint stress group; cP < 0.01 vs chronic restraint stress + dextran sodium sulfate group; fP < 0.05 vs control group; gP < 0.05 vs chronic restraint stress group; hP < 0.05 vs chronic restraint stress + dextran sodium sulfate group; jP < 0.05 vs dextran sodium sulfate group. CUMS: Chronic restraint stress; DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate; LD: Low-dose Wuling powder; MD: Medium-dose Wuling powder; HD: High-dose Wuling powder; FLU: Fluoxetine; MS: Mesalazine; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Wang JJ, Fan YH, Cao WT, Huang R, Yao XY, Li ML. Mechanism of Wuling powder modulating proBDNF/p75NTR/sortilin and BDNF/TrkB pathways in the treatment of ulcerative colitis complicated with depression. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(8): 100227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i8/100227.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100227