Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2025; 31(8): 100069
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069
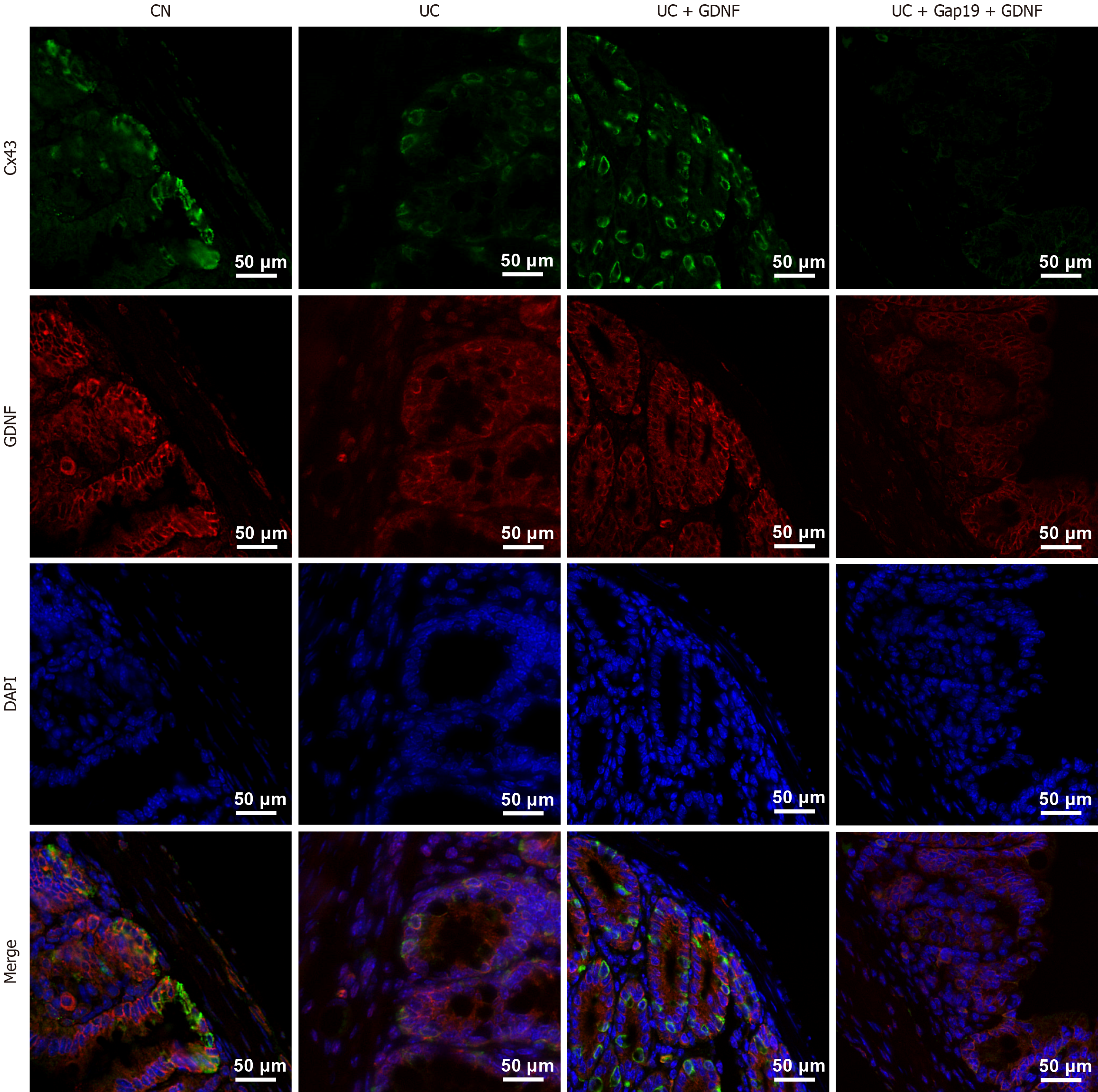
Figure 5 Dual-labelling immunofluorescence analysis of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in colonic tissues.
Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (red), connexin 43 (green), and 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue) in colonic tissues from different groups. Merged images showed the co-localization of connexin 43 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Scale bar: 50 μm. GDNF: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CN: Normal control; Cx43: Connexin 43; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Yang W, Liu R, Xu F. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor improves impaired colonic motility in experimental colitis mice through connexin 43. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(8): 100069
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i8/100069.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i8.100069