Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2025; 31(7): 98852
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98852
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98852
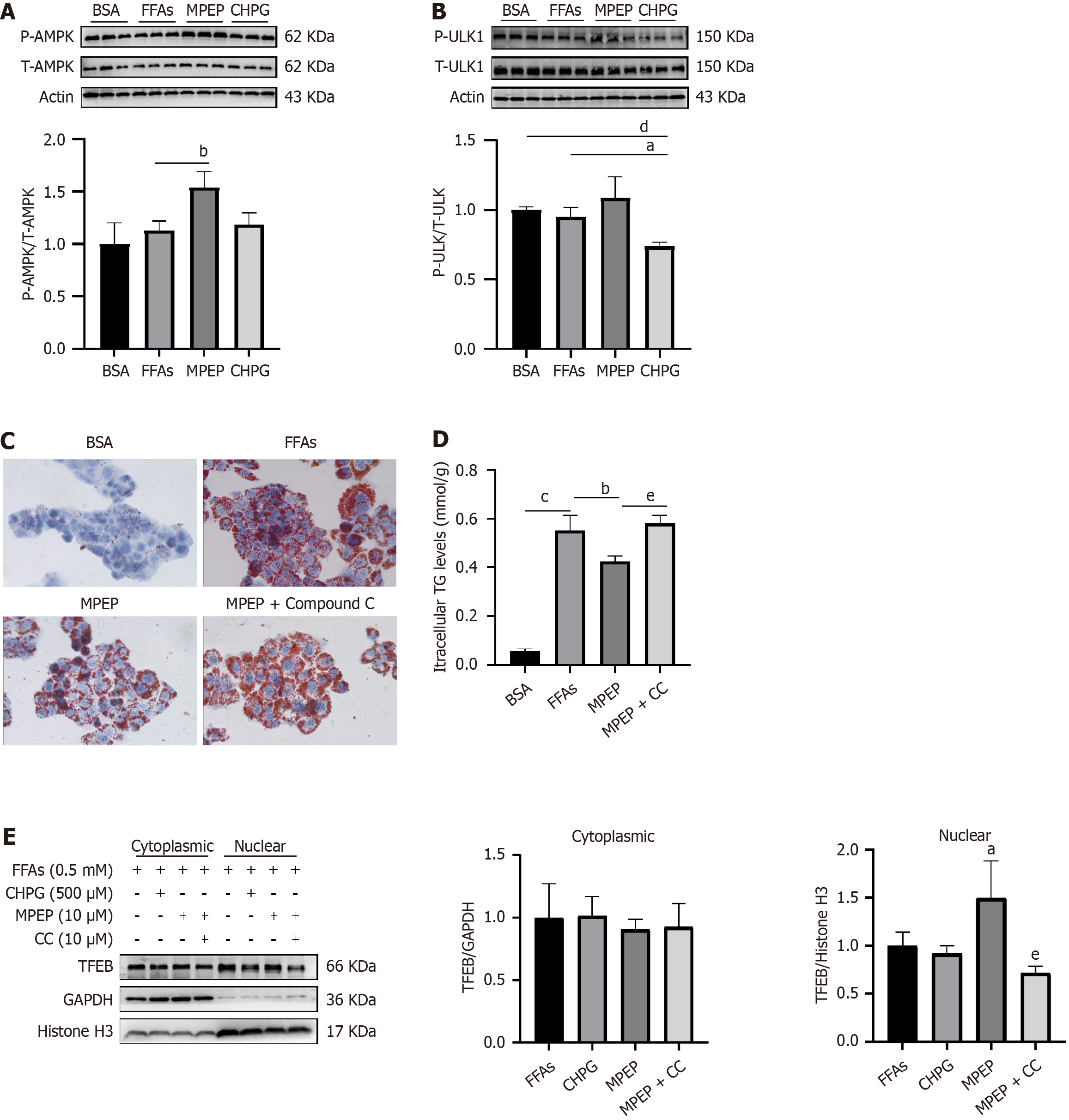
Figure 3 Inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5-induced autophagy via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway.
A and B: HepG2 cells were stimulated with 0.5 mmol/L free fatty acids (FFAs) for 24 hours and then treated with MPEP (10 μM) or CHPG (500 μM) for another 24 hours. Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression of P-AMPK, AMPK, P-ULK1 and ULK1 in the cells; C-E: HepG2 cells were stimulated with 0.5 mmol/L FFAs for 24 hours and then treated with MPEP (10 μM), CHPG or MPEP (10 μM) + Compound C (10 μM) for another 24 hours. The cells were stained with Oil Red O (C), and the level of intracellular triglyceride was quantitatively determined (D). Western blot was used to determine transcription factor EB expression in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of HepG2 cells (E). Histone H3 was used as a reference control for nuclear expression. aP < 0.05 vs free fatty acids; bP < 0.01 vs free fatty acids; cP < 0.001 vs bovine serum albumin; dP < 0.01 vs bovine serum albumin; eP < 0.01 vs MPEP. The data are presented as the mean ± SE. All cell experiments were repeated three times. FFAs: Free fatty acids; BSA: Bovine serum albumin; TFEB: Transcription factor EB.
- Citation: Tao M, Zhang LL, Zhou GH, Wang C, Luo X. Inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor-5 alleviates hepatic steatosis by enhancing autophagy via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(7): 98852
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i7/98852.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98852