Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2025; 31(6): 96782
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782
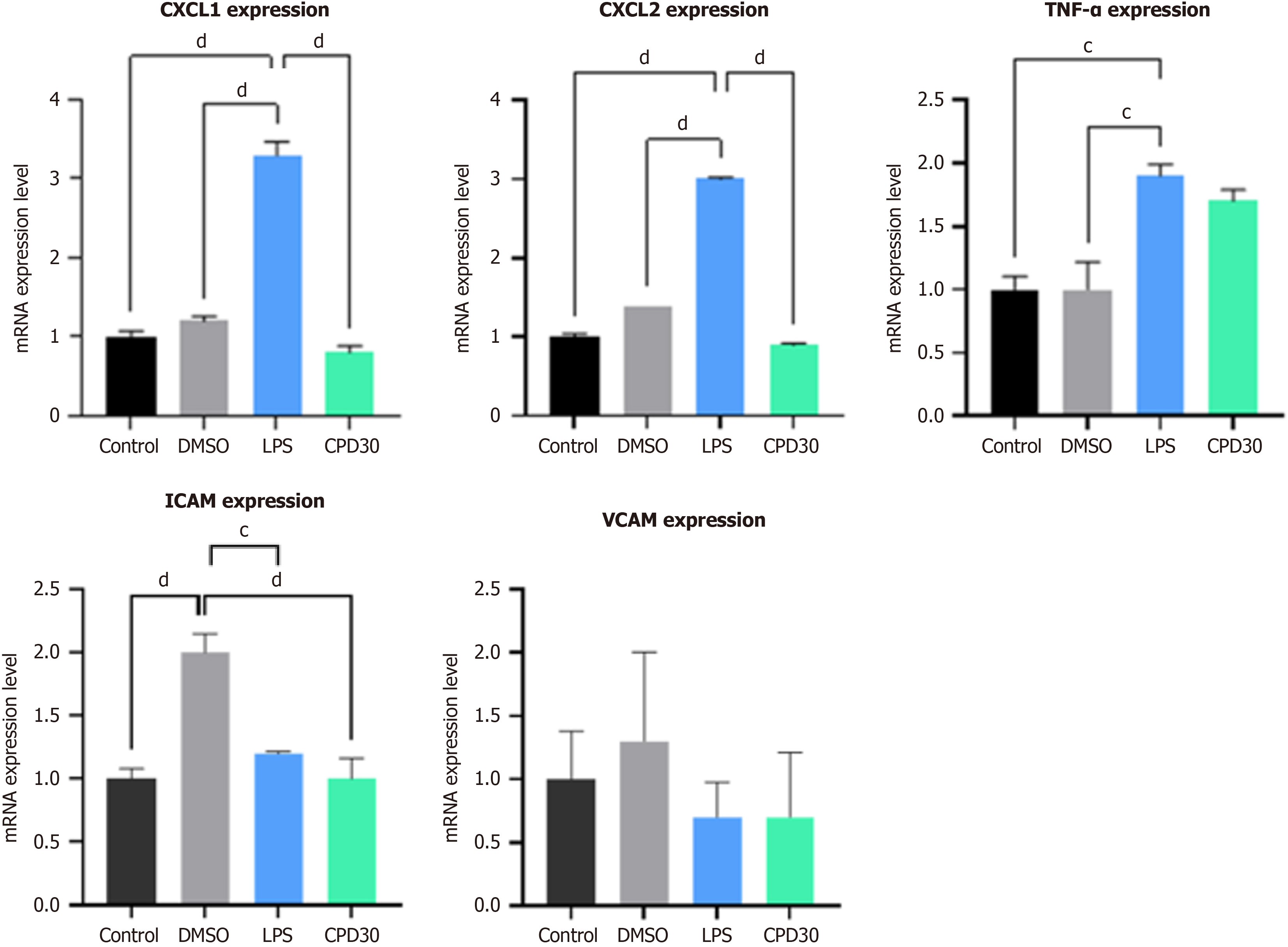
Figure 7 Effects of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein adenosine triphosphate pocket inhibitor on alcoholic liver disease model after lipopolysaccharide stimuli in liver organoid system.
Liver organoids were treated with lipopolysaccharide to create an alcohol-induced liver disease model. After mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein adenosine triphosphate pocket-binding inhibitor treatment after necroptotic stimuli, the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α, CXCL1/CXCL2, ICAM, and VCAM decreased in the organoid system. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; CPD: Compound.
- Citation: Xuan Yuan HN, Kim HS, Park GR, Ryu JE, Kim JE, Kang IY, Kim HY, Lee SM, Oh JH, Yoon EL, Jun DW. Adenosine triphosphate-binding pocket inhibitor for mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein attenuated alcoholic liver disease via necroptosis-independent pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(6): 96782
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i6/96782.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782