Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2025; 31(6): 96782
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782
Published online Feb 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782
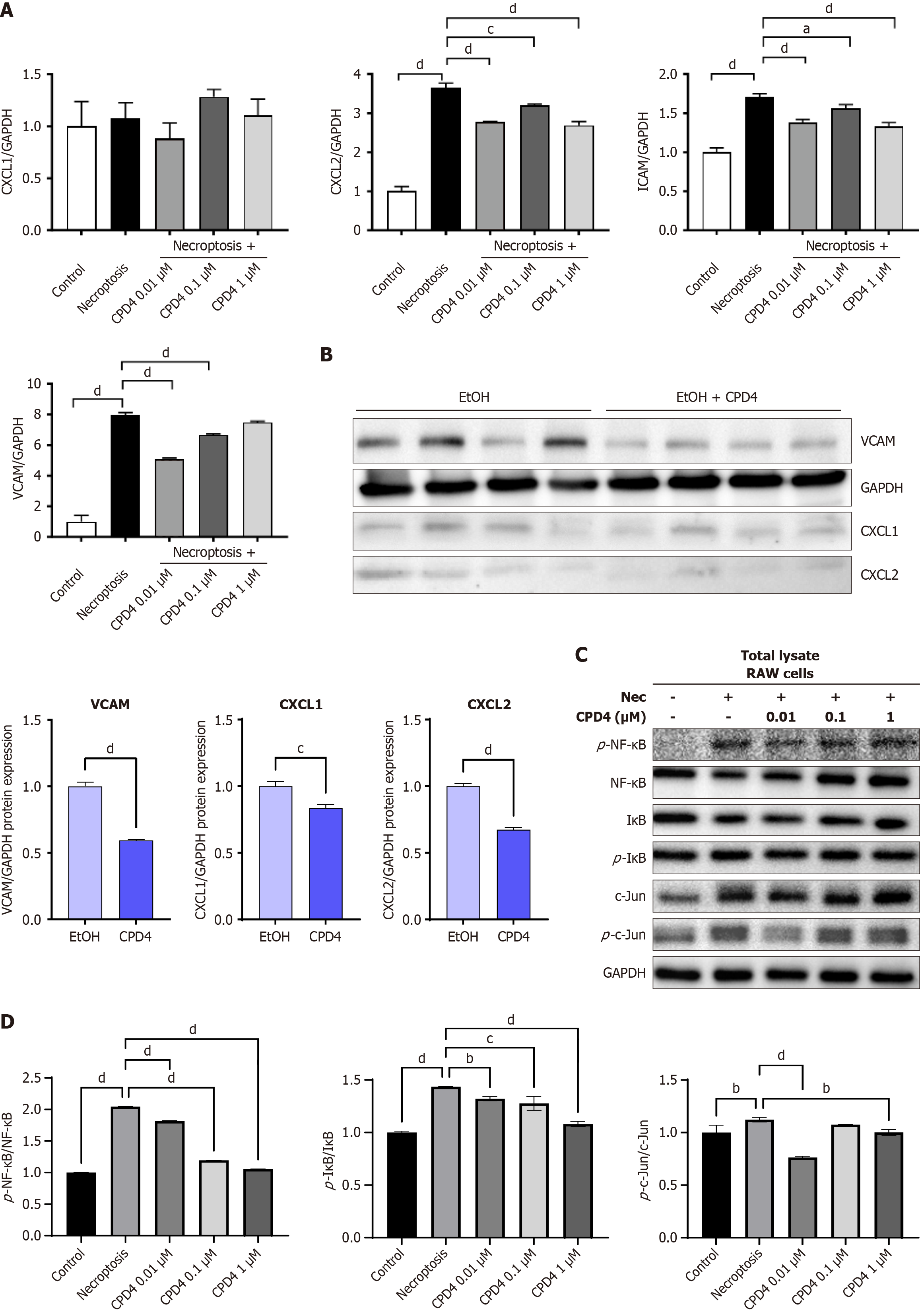
Figure 4 Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein adenosine triphosphate-binding inhibitor cannot evade cell death after necroptosis stimuli but inhibition of inflammation.
A: U937, HT29 and FADD cells treated with Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding inhibitor (Compound-4) to determine cell viability; B: After induction of necroptosis in RAW 264.7 cells, MLKL ATP-binding inhibitor was administered to measure CXCL1, CXCL2, ICAM, and VCAM mRNA expression levels via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C and D: Western blot analysis of phosphorylated-nuclear factor kappa-B, nuclear factor kappa-B, phospho-c-Jun, c-Jun, I-kappa-B-alpha, phospho-I-kappa-B-alpha, c-Jun N-terminal kinases and phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinases protein expression in RAW 264.7 cells after compound-4 treatment. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CPD4: Compound-4; EtOH: Ethyl alcohol.
- Citation: Xuan Yuan HN, Kim HS, Park GR, Ryu JE, Kim JE, Kang IY, Kim HY, Lee SM, Oh JH, Yoon EL, Jun DW. Adenosine triphosphate-binding pocket inhibitor for mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein attenuated alcoholic liver disease via necroptosis-independent pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(6): 96782
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i6/96782.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.96782