Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
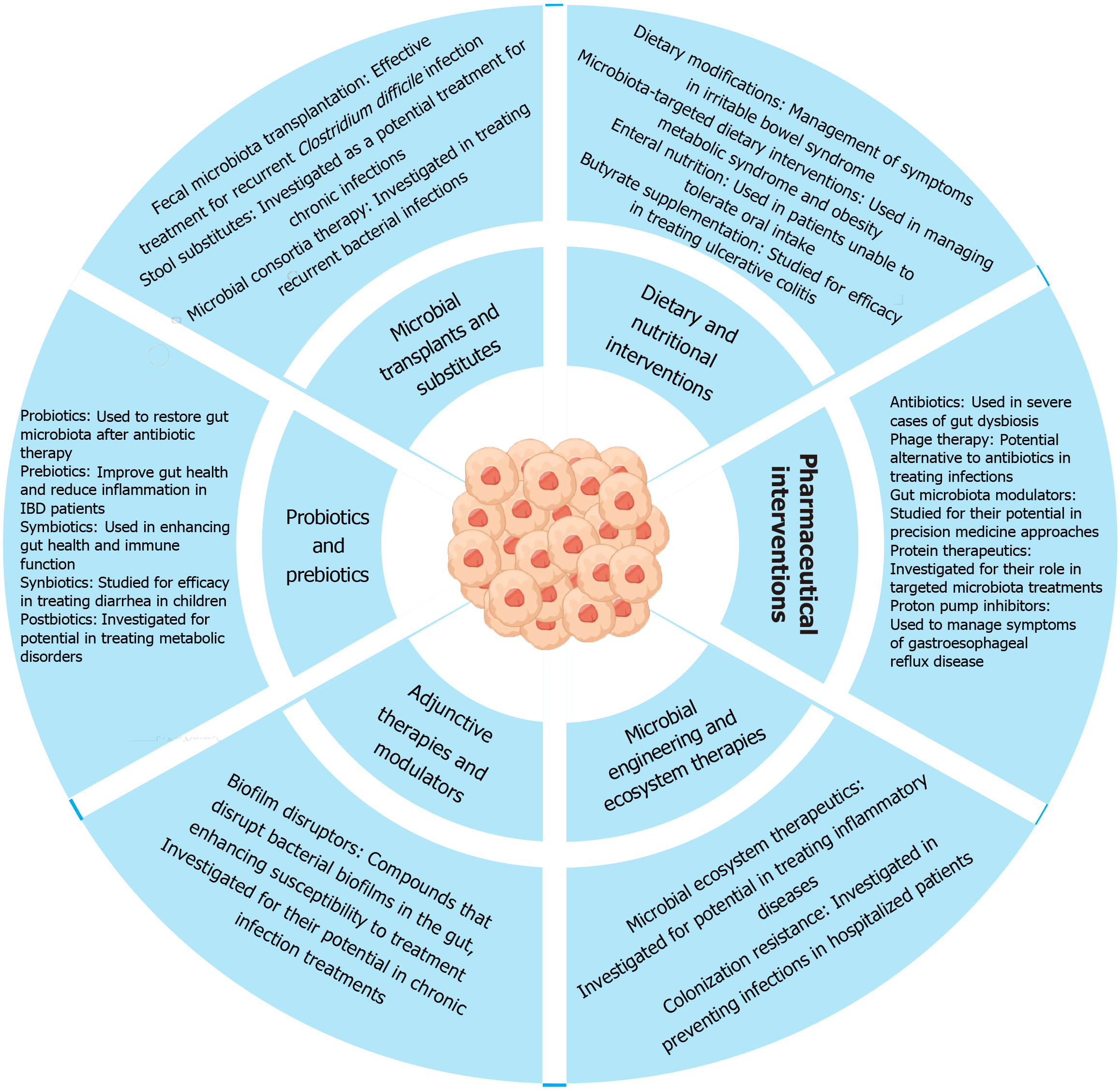
Figure 4 Therapeutic strategies aimed at improving gut health through different interventions.
The section on “Microbial transplants and substitutes” highlights the use of fecal microbiota transplantation stool substitutes, and microbial consortia for treating recurrent infections and metabolic disorders. “Probiotics and prebiotics” are emphasized for restoring and enhancing gut microbiota, improving gut health, and reducing inflammation, with specific applications for inflammatory bowel disease and metabolic disorders. “Dietary and nutritional interventions” include dietary modifications, microbiota-targeted diets, enteral nutrition, and butyrate supplementation for managing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. The “Pharmaceutical interventions” segment lists antibiotics, phage therapy, gut microbiota modulators, protein therapeutics, and proton pump inhibitors for treating dysbiosis and other gut-related conditions. “Adjunctive therapies and modulators” feature biofilm disruptors for treating chronic infections, while “Microbial engineering and ecosystem therapies” focus on microbial ecosystem therapeutics and colonization resistance to prevent infections and manage inflammatory diseases.
- Citation: Paul JK, Azmal M, Haque ASNB, Meem M, Talukder OF, Ghosh A. Unlocking the secrets of the human gut microbiota: Comprehensive review on its role in different diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 99913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/99913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913