Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
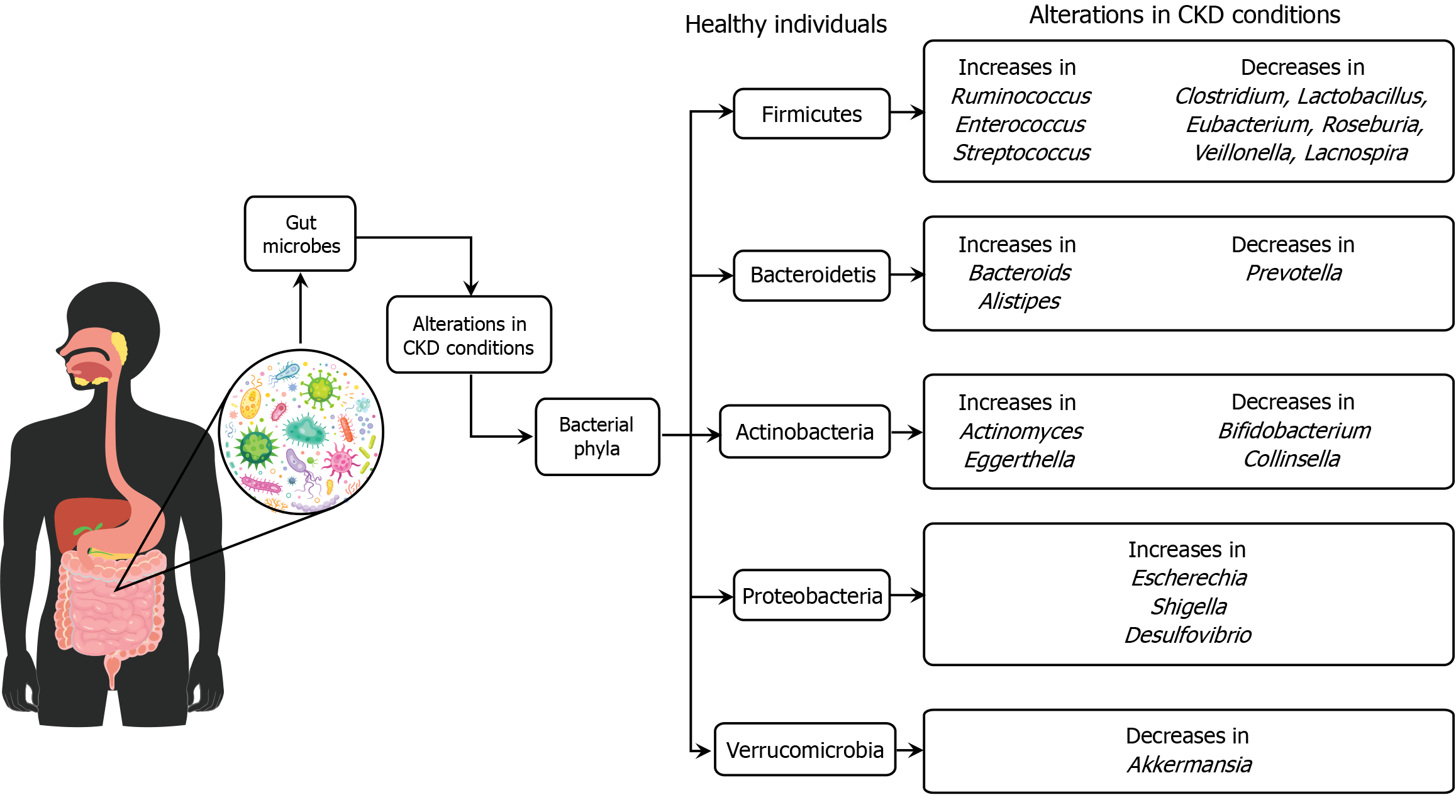
Figure 3 The alterations in gut microbiota are associated with chronic kidney disease conditions compared to healthy individuals.
In chronic kidney disease, there is a notable shift in the abundance of various bacterial phyla. Specifically, certain bacteria, such as Ruminococcus and Enterococcus from the Firmicutes phylum, are increased, while beneficial bacteria like Clostridium and Lactobacillus are decreased. Similar patterns are observed in other phyla, with increases in some bacteria and decreases in others, indicating a state of dysbiosis. This microbial imbalance is important as it may influence chronic kidney disease progression and related complications, highlighting the role of gut microbiota in disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. CKD: Chronic kidney disease.
- Citation: Paul JK, Azmal M, Haque ASNB, Meem M, Talukder OF, Ghosh A. Unlocking the secrets of the human gut microbiota: Comprehensive review on its role in different diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 99913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/99913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913