Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
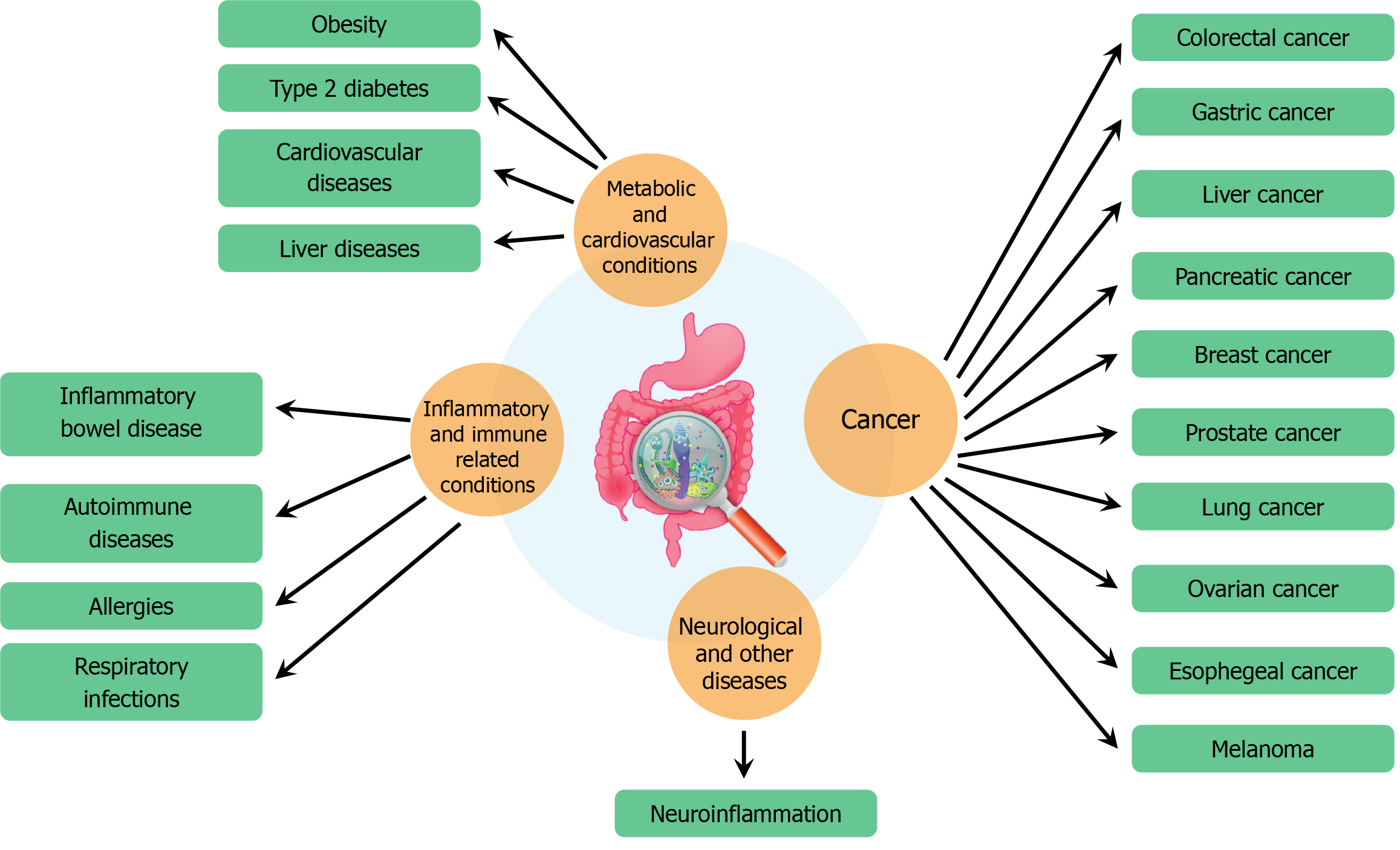
Figure 2 The relationship between human health and various diseases.
It highlights how poor gut health is linked to a range of conditions across different categories. Metabolic and cardiovascular conditions associated with gut health include obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and liver diseases. Inflammatory and immune-related conditions affected by gut health include inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune diseases, allergies, and respiratory infections. Gut health also plays a role in the development of cancer, with potential links to colorectal, gastric, liver, pancreatic, breast, prostate, lung, ovarian, esophageal cancers, and melanoma. Additionally, gut health is connected to neurological and other diseases, notably through neuroinflammation, emphasizing the extensive impact of gut microbiota on overall health.
- Citation: Paul JK, Azmal M, Haque ASNB, Meem M, Talukder OF, Ghosh A. Unlocking the secrets of the human gut microbiota: Comprehensive review on its role in different diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 99913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/99913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913