Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913
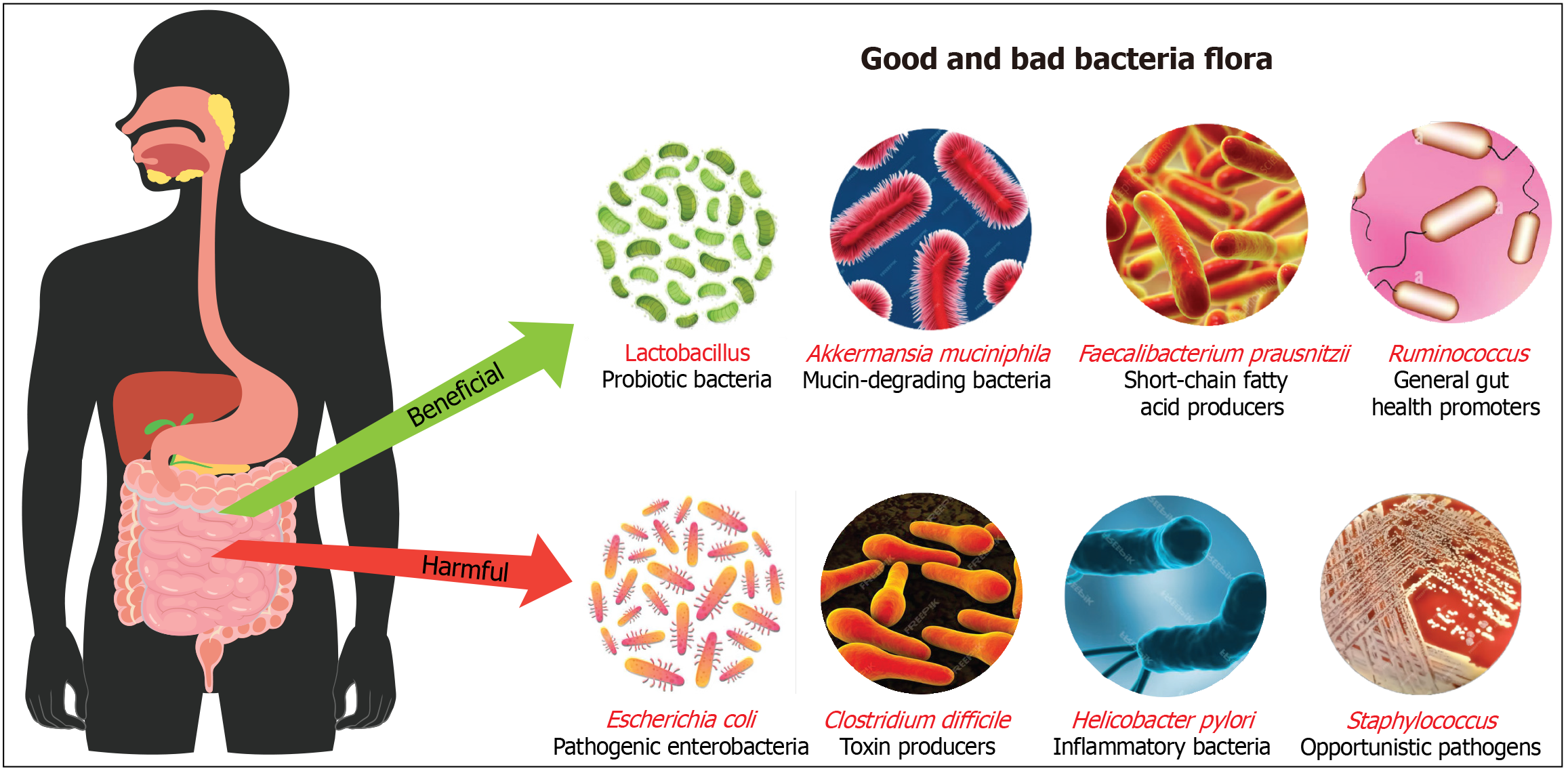
Figure 1 Illustration to distinguish between beneficial and harmful gut bacteria.
Beneficial bacteria include Lactobacillus, which are probiotics supporting digestion and immunity; Akkermansia muciniphila, which maintains gut lining integrity; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, short-chain fatty acid producers with anti-inflammatory effects; and Ruminococcus, which aid in digesting complex carbohydrates. In contrast, harmful bacteria such as Escherichia coli can cause infections, Clostridium difficile produce toxins linked to severe diarrhea, Helicobacter pylori are associated with stomach ulcers, and Staphylococcus can be opportunistic pathogens. This highlights the critical role of a balanced microbiome in health maintenance and disease prevention.
- Citation: Paul JK, Azmal M, Haque ASNB, Meem M, Talukder OF, Ghosh A. Unlocking the secrets of the human gut microbiota: Comprehensive review on its role in different diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 99913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/99913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.99913