Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 98732
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.98732
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.98732
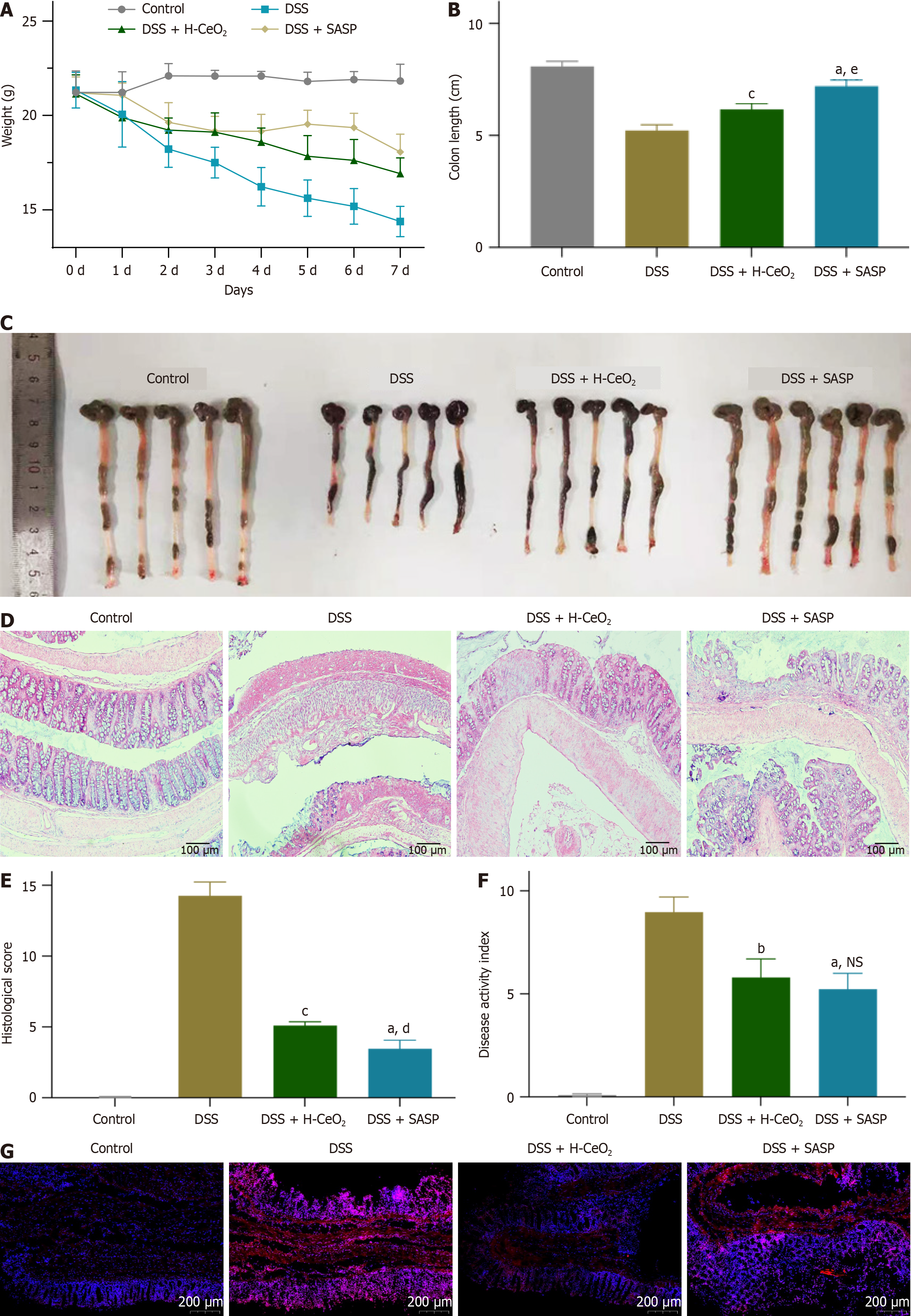
Figure 4 Hollow cerium inhibits occurrence and development of colitis in mice by scavenging reactive oxygen species.
A-C: Hollow cerium nanoparticles (H-CeO2) treatment reduced the changes in weight (A) and colon length (B and C) of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis mice; D and E: Hematoxylin and eosin detected the effect of H-CeO2 treatment on the histopathology of the colon in DSS-induced mice; F: H-CeO2 treatment reduces disease activity index values in DSS-induced mice; G: H-CeO2 treatment reduced reactive oxygen species levels in DSS-induced mouse tissues. Cell nuclei stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue), and intracellular reactive oxygen species levels were quantitated in dihydroethidium (red). aP < 0.001 vs control group; bP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium group; cP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium group; dP < 0.01 vs dextran sulfate sodium + hollow cerium nanoparticles group; eP < 0.001 vs dextran sulfate sodium + hollow cerium nanoparticles group; NS indicates statistical difference. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; H-CeO2: Hollow cerium; SASP: Sulfasalazine; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Mi L, Zhang K, Ma JX, Yao JF, Tong YL, Bao ZJ. Hollow cerium nanoparticles synthesized by one-step method for multienzyme activity to reduce colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 98732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/98732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.98732