Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 101722
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101722
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101722
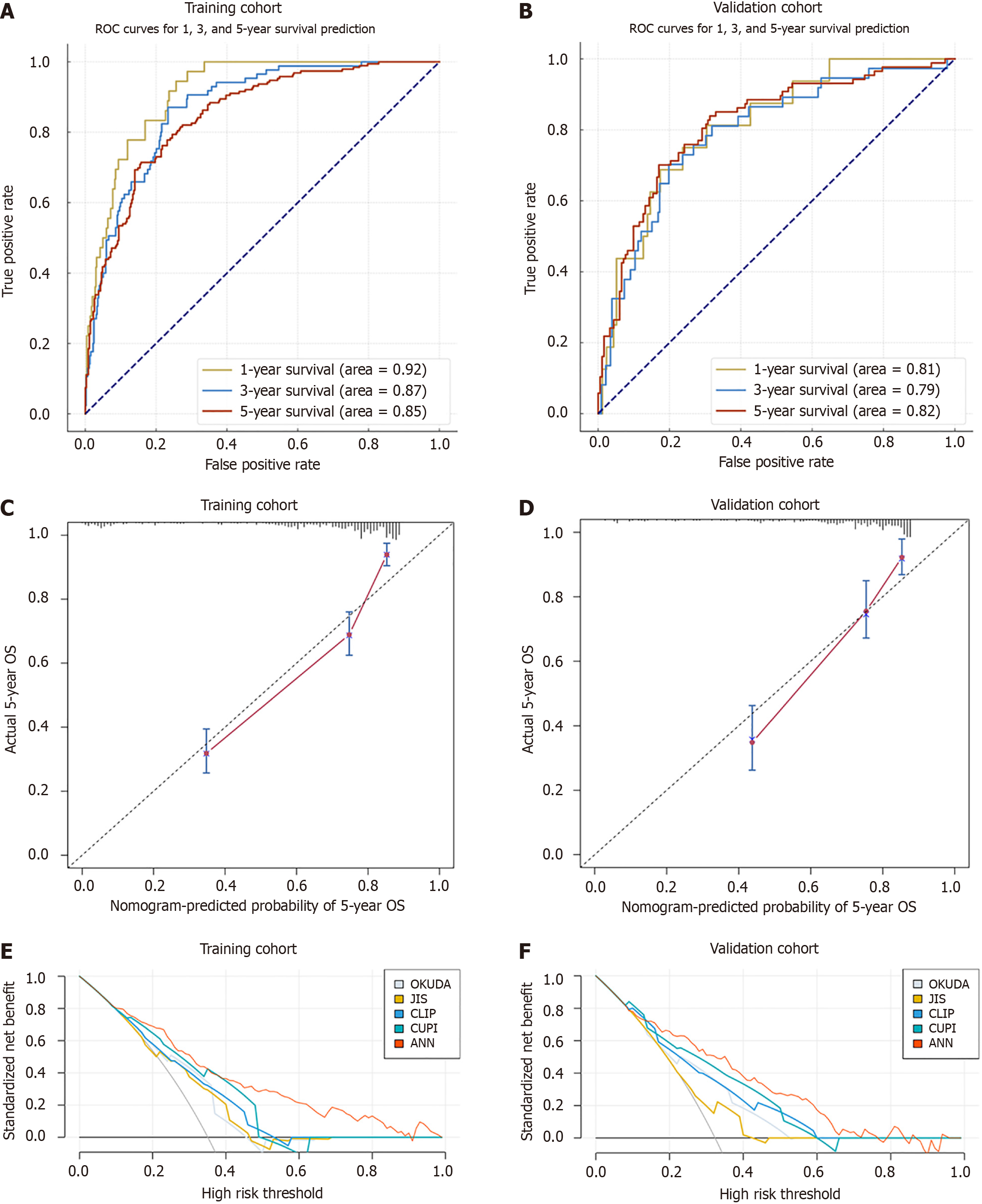
Figure 3 Evaluation of the predictive performance of the artificial neural networks model.
A and B: The area under the curve of the artificial neural networks in prediction of 1-, 3-, and 5-year mortality in the training cohort (A) and validation cohort (B); C and D: Calibration curves for predicting 5-year overall survival in the training cohort (C) and validation cohort (D); E and F: The decision curve analysis for predicting 5-year mortality in the training cohort (E) and validation cohort (F). ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; OS: Overall survival; RSF: Random forest analysis. ANN: Artificial neural network; RSF: Random survival forest; JIS: Japan integrated staging score; Okuda: Okuda staging system; CUPI: Chinese university prognostic index; CLIP: Cancer of the liver Italian program.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Shi K, Feng Y, Wang XB. Machine learning model using immune indicators to predict outcomes in early liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 101722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/101722.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101722