Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2025; 31(5): 101280
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101280
Published online Feb 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101280
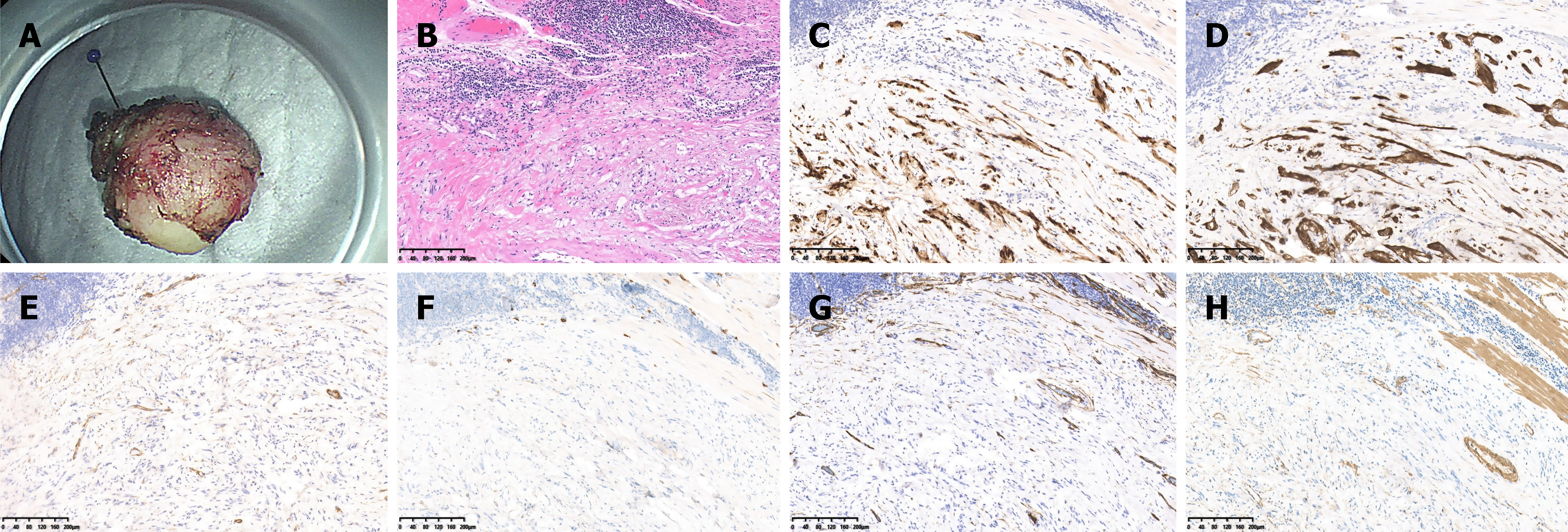
Figure 4 Gross and pathological findings of esophageal schwannoma resection via submucosal tunnel endoscopic resection (from the first patient shown in the previous endoscopic images).
A: Endoscopic imaging showing a solid tumor measuring 1.4 cm × 1.2 cm × 0.8 cm; B: Pathological examination revealing that the tumor was composed of bland spindle cells (hematoxylin and eosin, 100 ×) with chronic inflammatory cell infiltration around the tumor; C and D: Positive immunohistochemical staining of SOX-10 and S-100 (magnification, 100 ×); E-G: Negative immunohistochemical staining of DOG-1, CD-117, and CD34 (magnification, 100 ×); H: Slightly positive immunohistochemical staining for SMA.
- Citation: Zhang PC, Wang SH, Li J, Wang JJ, Chen HT, Li AQ. Clinicopathological features and treatment of gastrointestinal schwannomas. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(5): 101280
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i5/101280.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i5.101280