Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2025; 31(4): 93179
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179
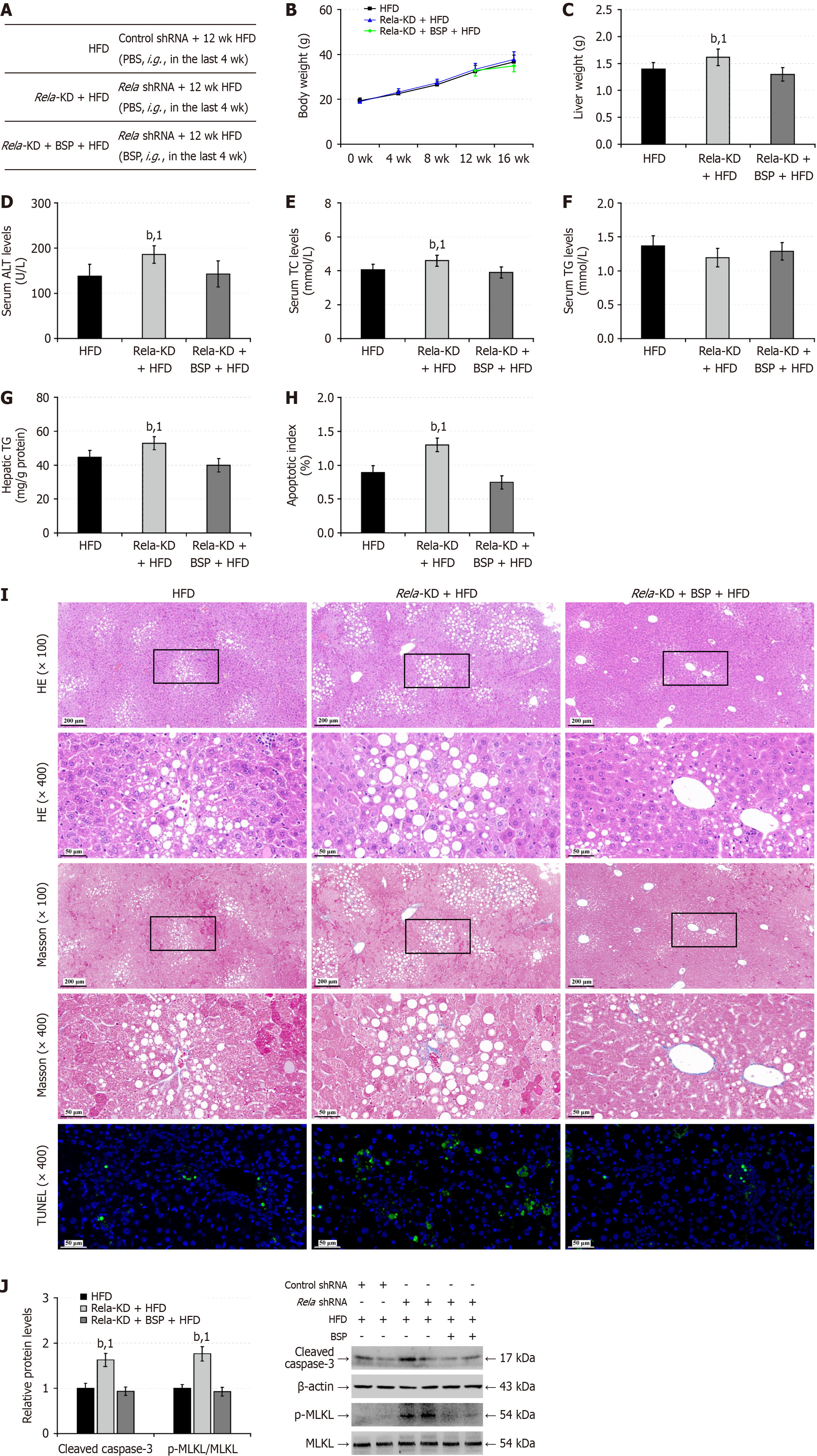
Figure 9 RELA silencing partially abrogates the therapeutic effects of Bletilla striata polysaccharides on hepatic steatosis in mice.
A: C57BL/6 mice were treated intravenously with recommended adeno-associated virus virions for the expression of control shRNA or RELA-specific shRNA and four weeks later, they were fed with high-fat-diet (HFD) for 12 weeks. During the last 4-week of HFD feeding, the RELA silencing mice were randomized and treated with vehicle phosphate buffer saline or Bletilla striata polysaccharides (BSP) for 4 weeks, leading to the HFD, RELA-knockdown (KD) + HFD group, and RELA-KD + BSP + HFD groups (n = 12); B: Mouse body weights; C: Liver weights; D: Serum aminotransferase levels; E: Serum total cholesterol levels; F: Serum triglyceride (TG) levels; G: Liver tissue TG contents; H: Apoptotic index; I: Hematoxylin and eosin and Masson staining of liver tissue sections and transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labeling analysis of liver cell apoptosis; J: Western blot analysis of the relative levels of hepatic cleaved caspase-3, and mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein phosphorylation. Data are representative images or expressed as the mean ± SD of each group of mice from three separate experiments. bP < 0.01. 1P < 0.01 vs the high-fat-diet group. BSP: Bletilla striata polysaccharides; TG: Triglycerides; KD: Knockdown; HFD: High-fat-diet; wk: Week; shRNA: Small hairpin ribonucleic acid; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglycerides; MLKL: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; qd: Quaque die; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labeling.
- Citation: He YH, Ou LL, Jiang JL, Chen YF, Abudukeremu A, Xue Y, Mu MY, Zhong WW, Xu DL, Meng XY, Guan YQ. Bletilla striata polysaccharides alleviate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through enhancing hepatocyte RelA/ HNF1α signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(4): 93179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i4/93179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179