Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2025; 31(4): 93179
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179
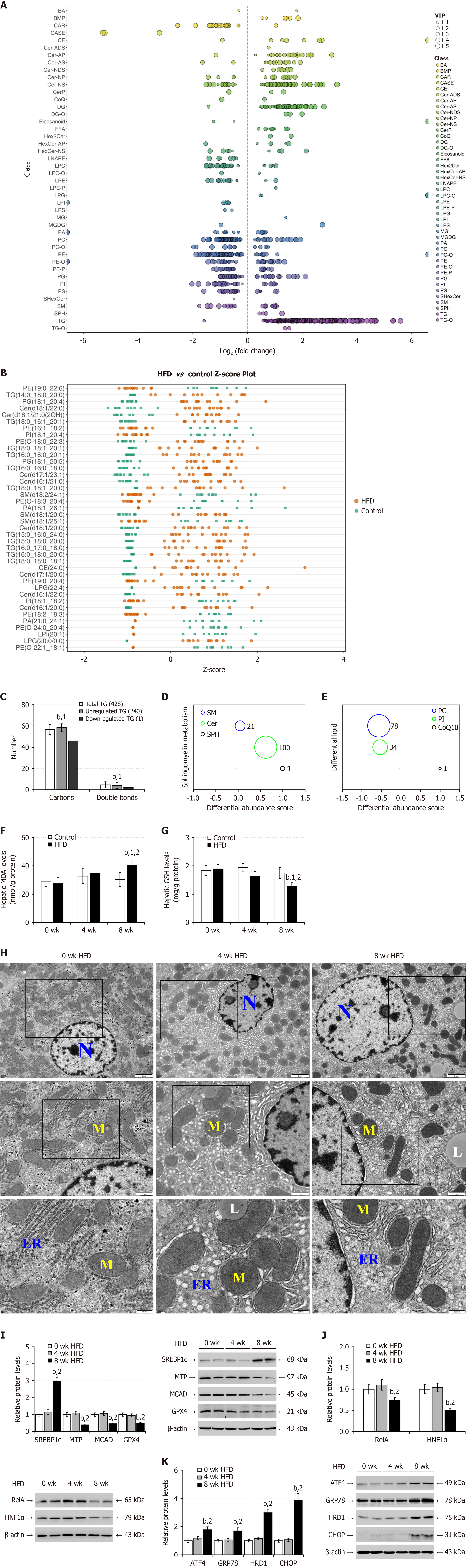
Figure 2 Lipid metabolism remodeling, and nuclear factor kappa B p65/hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha signaling damage in mouse liver with steatosis.
Liver lipids were extracted from the control and high-fat-diet-fed mice and subjected to liposome analyses using extensive targeted lipidomics techniques. The underlying causes of lipid metabolism remodeling and validation of differential lipid biological functions were explored. A: A scatter plot of differential lipids; B: Z-value plot of differential lipids; C: The number of triglycerides with average carbon atom and double bonds; D: Differential abundance scores of the sphingolipid metabolism pathway. The size of the circles represents the number of differential lipid species; E: Differential abundance scores of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol and reduced coenzyme Q10; F: Hepatic malondialdehyde levels; G: Hepatic reduced glutathione levels; H: Transmission electron microscopy analysis of liver tissue ultrastructure; I: Western blot analysis of the relative levels of lipid metabolism-related protein expression; J: Western blot analysis of nuclear factor kappa B p65, and hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha protein expression; K: Western blot analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related protein expression levels. Data are representative images or expressed as the mean ± SD of each group (n = 10-12) of mice from at least three separate experiments. bP < 0.01. 1P < 0.01 vs the corresponding control or total triglycerides group. 2P < 0.01 vs the 0-week group. HFD: High-fat-diet; TG: Triglycerides; SM: Sphingomyelin; Cer: Ceramide; SPH: Sphingosine; PC: Phosphatidylcholine; PI: Phosphatidylinositol; CoQ10: Reduced coenzyme Q10; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; L: Lipid droplet; M: Mitochondria; N: Nucleus; VIP: Variable importance in projection; wk: Week; SREBP1c: Cleaved sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; MTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; MCAD: Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; HNF1α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha; GRP78: 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein; CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; HRD1: 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase degradation 1 homolog; ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; RelA: Nuclear factor kappa B p65.
- Citation: He YH, Ou LL, Jiang JL, Chen YF, Abudukeremu A, Xue Y, Mu MY, Zhong WW, Xu DL, Meng XY, Guan YQ. Bletilla striata polysaccharides alleviate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through enhancing hepatocyte RelA/ HNF1α signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(4): 93179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i4/93179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.93179