Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2025; 31(4): 100470
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100470
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100470
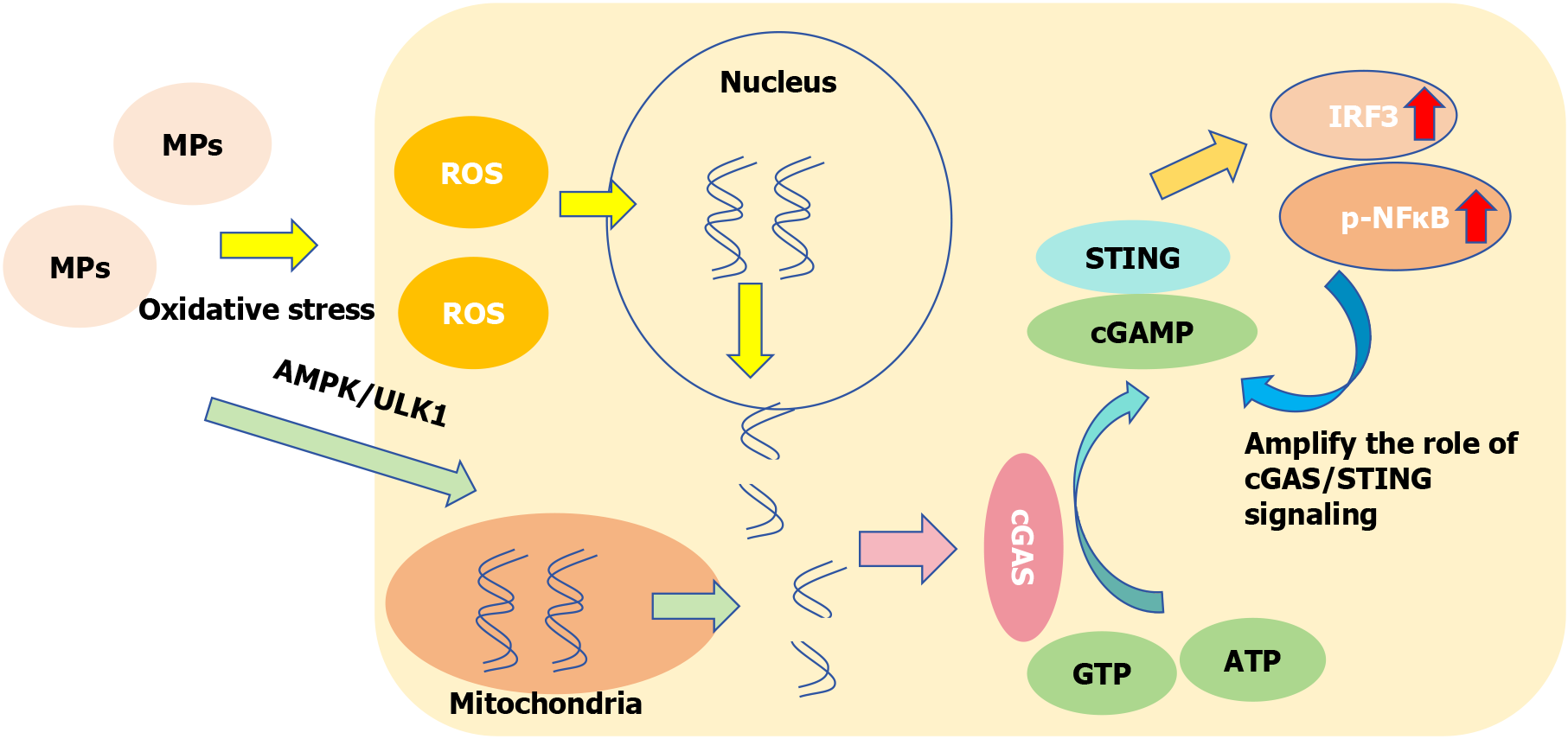
Figure 6 The role that microplastics play in the cGAS/STING pathway.
Microplastics induce oxidative stress, produce a large number of reactive oxygen species, damage DNA in the nucleus, and induce mitochondrial autopahgy. Damaged DNA enters the cytoplasm and interacts with double-stranded DNA sensor cGAS to catalyse guanosine triphosphate and adenosine triphosphate to form cyclic GMP-AMP. Cyclic GMP-AMP binds to STING homomeric diplosomes to activate downstream pathway and induce increased expression of transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 3 and phosphorylated nuclear factor-kappaB. Phosphorylated nuclear factor-kappaB, in turn, amplifies the action of the cGAS/STING signal. MPs: Microplastics; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; AMPK: Adenosine5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; ULK1: UNC-51-like kinase; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; p-NFκB: Phosphorylated nuclear factor-kappaB; cGAMP: Cyclic GMP-AMP; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate.
- Citation: Wang YF, Wang XY, Chen BJ, Yang YP, Li H, Wang F. Impact of microplastics on the human digestive system: From basic to clinical. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(4): 100470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i4/100470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100470