Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2025; 31(4): 100401
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401
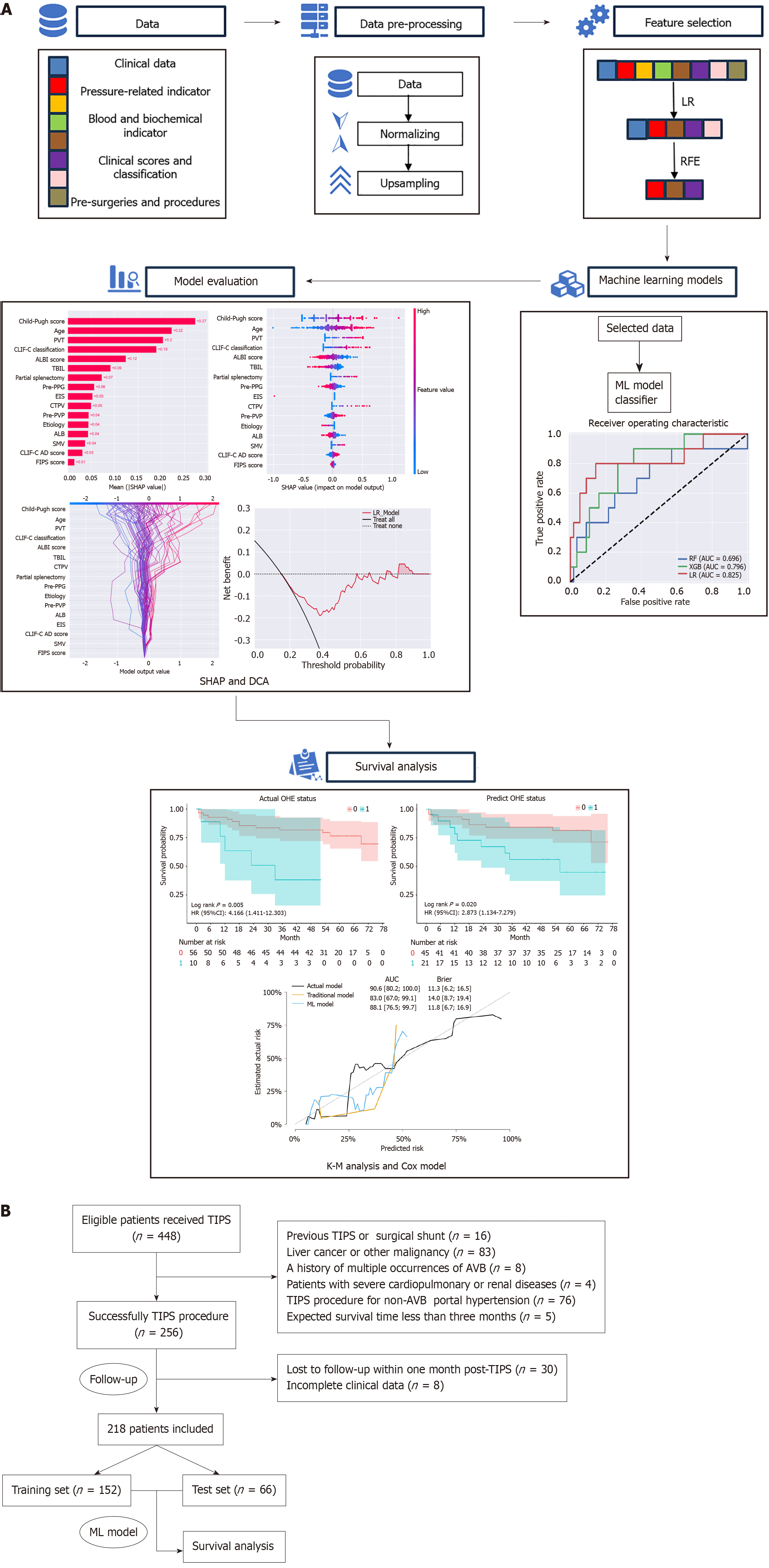
Figure 1 Study design.
A: Development and validation of the overt hepatic encephalopathy prediction model; B: Flowchart of patient enrollment and grouping. LR: Logistic regression; RFE: Recursive feature elimination; K-M: Kaplan-Meier; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations; DCA: Decision curve analysis; AVB: Acute variceal bleeding; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; ML: Machine learning.
- Citation: Liu DJ, Jia LX, Zeng FX, Zeng WX, Qin GG, Peng QF, Tan Q, Zeng H, Ou ZY, Kun LZ, Zhao JB, Chen WG. Machine learning prediction of hepatic encephalopathy for long-term survival after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in acute variceal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(4): 100401
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i4/100401.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i4.100401