Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 99082
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.99082
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.99082
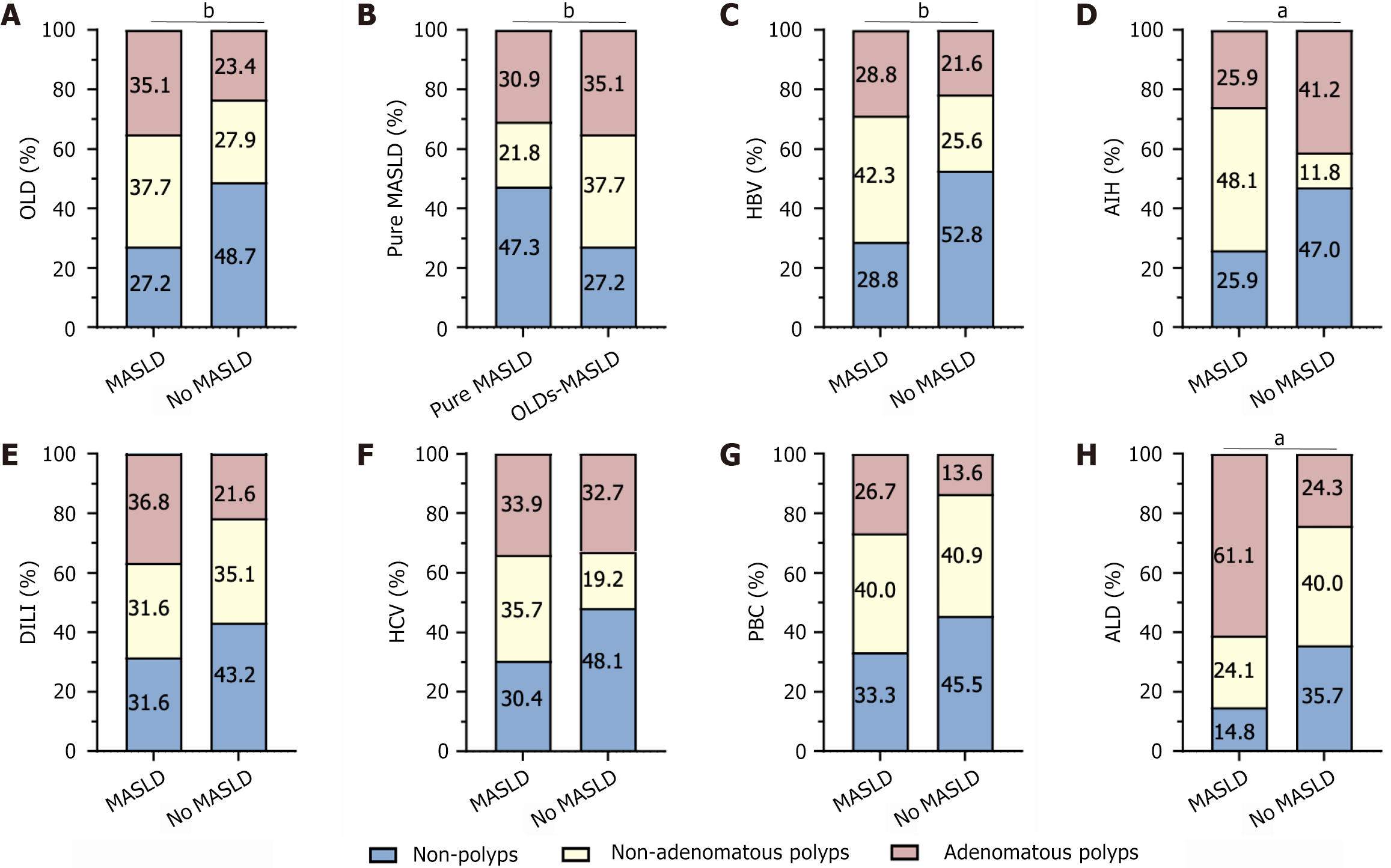
Figure 5 Percentage of chronic liver disease etiology combined with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and no metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
A: Other liver diseases; B: Pure metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; C: Hepatitis B virus; D: Autoimmune hepatitis; E: Drug-induced liver injury; F: Hepatitis C virus; G: Primary biliary cholangitis; H: Alcoholic liver disease. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. OLD: Other liver diseases; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; DILI: Drug-induced liver injury; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis; ALD: Alcoholic liver disease.
- Citation: Li YQ, Kuai WT, Chen L, Zeng MH, Tao XM, Han JX, Wang YK, Xu LX, Ge LY, Liu YG, Li S, Xu L, Mi YQ. Predicting colorectal adenomatous polyps in patients with chronic liver disease: A novel nomogram. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 99082
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/99082.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.99082