Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 101180
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.101180
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.101180
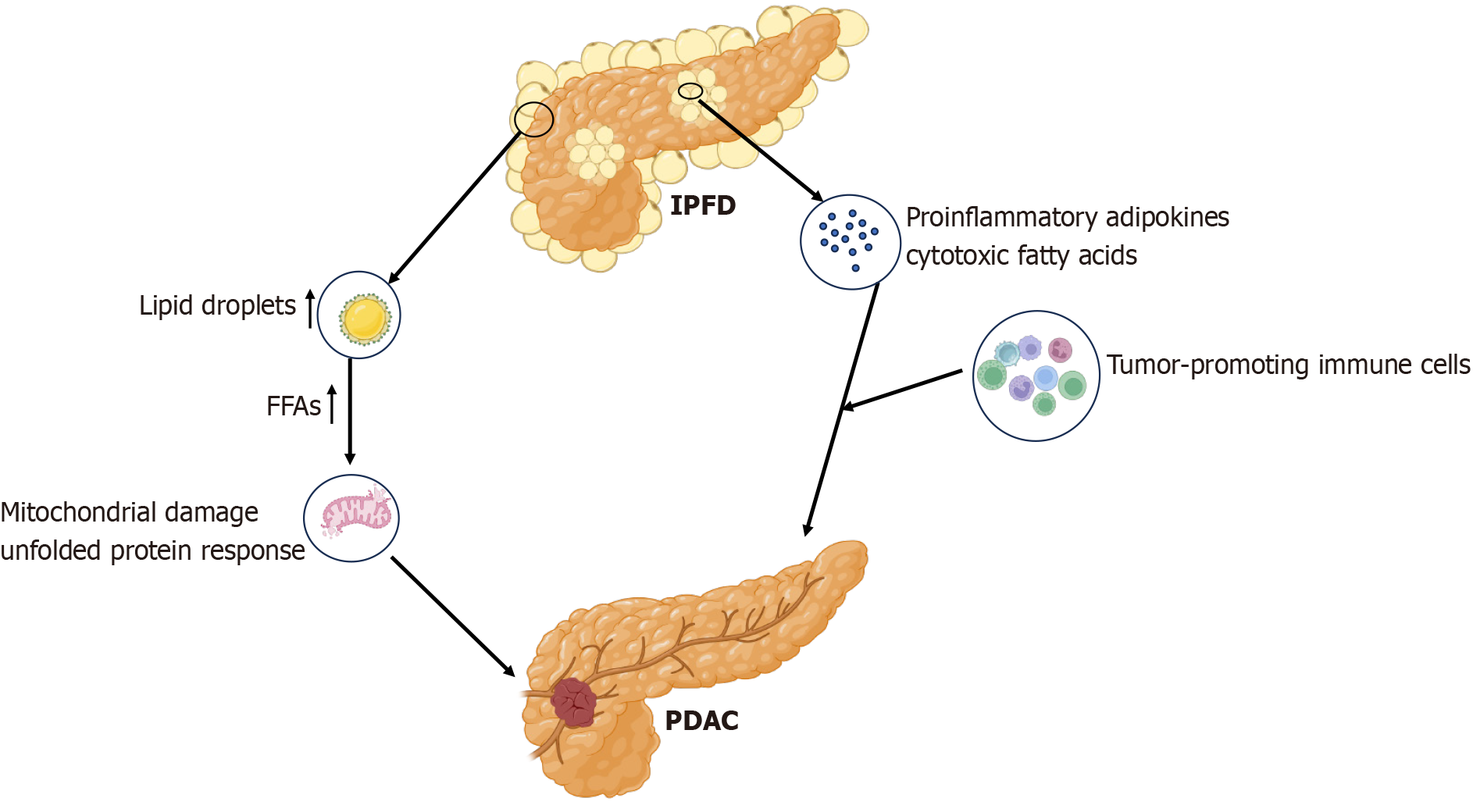
Figure 2 Mechanism of intrapancreatic fat deposition-induced pancreatic cancer.
During intrapancreatic fat deposition, the accumulation of intracellular lipid droplets leads to an elevation in toxic free fatty acids, which induces mitochondrial dysfunction and triggers the unfolded protein response. These events contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer. Moreover, pro-inflammatory cytokines and cytotoxic fatty acids released by pancreatic adipocytes in the intrapancreatic fat deposition environment foster an inflammatory microenvironment. This microenvironment facilitates the proliferation of transformed cells with carcinogenic potential by promoting the recruitment of tumor-supportive immune cells. IPFD: Intrapancreatic fat deposition; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; FFA: Free fatty acid.
- Citation: Ye J, Wang JG, Liu RQ, Shi Q, Wang WX. Association between intra-pancreatic fat deposition and diseases of the exocrine pancreas: A narrative review. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 101180
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/101180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.101180