Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
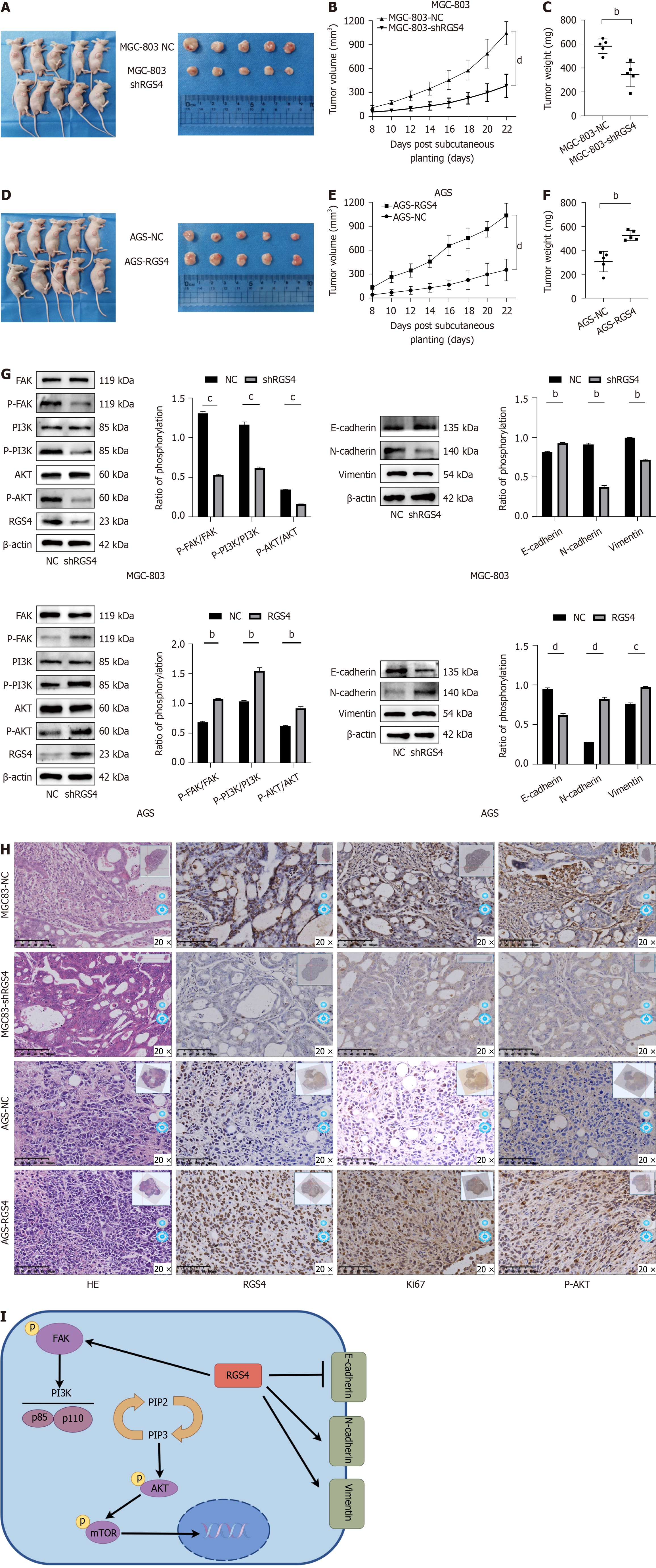
Figure 5 Knocking down regulator of G protein signaling 4 in gastric cancer cells inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
A-F: Tumors from MGC-803 cells with regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) knockdown and AGS cells with RGS4 overexpression and their controls (n = 5/groups) (A and D), tumor growth curves (B and E), tumor weight of each group (C and F); G: The expression of focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial mesenchymal transition related proteins in MGC-803 cells and AGS cells in vivo were validated by western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control; H: The expression of RGS4, Ki67 and p-AKT in these xenografts via immunohistochemistry staining; I: Schematic diagram of the mechanism of RGS4 promoting gastric cancer progression. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.0001. FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4; PIP: Prolactin-induced protein; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Chen PY, Wang PY, Liu B, Jia YP, Zhang ZX, Liu X, Wang DH, Yan YJ, Fu WH, Zhu F. RGS4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 100898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/100898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898