Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
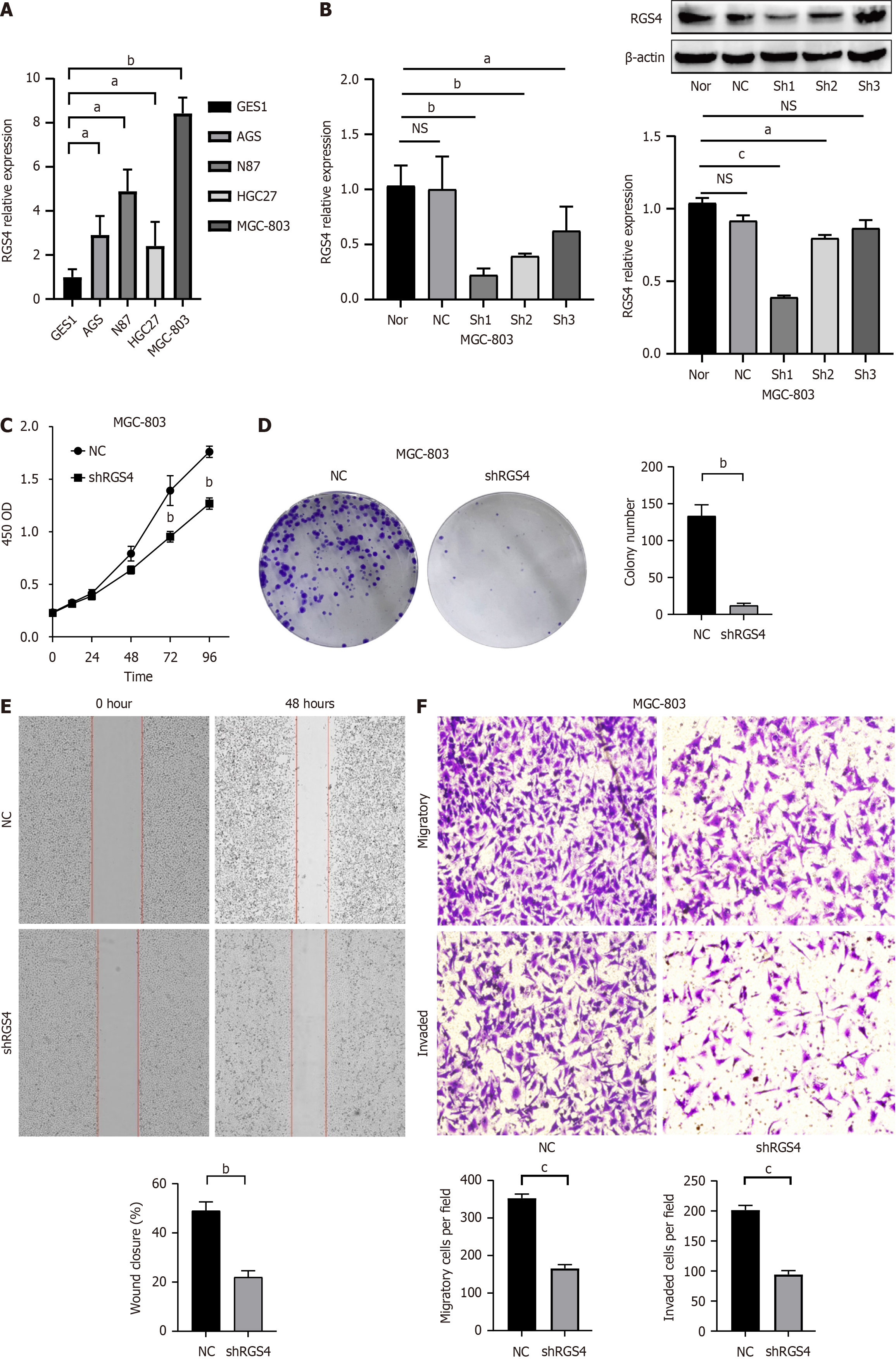
Figure 2 Regulator of G protein signaling 4 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro.
A: The expression levels of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in different gastric cancer (GC) cell lines were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; B: The interference efficiency of the lentiviral human RGS4-targeting short hairpin RNA was validated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (left) and western blot (right) analysis; C: The proliferation of MGC-803 cells with RGS4 knockdown was determined by cell counting kit-8 assays; D: The effects of RGS4 knockdown on the colony formation of MGC-803 cells; E: The migration ability of MGC-803 cells was measured by wound healing; F: The invasion of MGC-803 cells with RGS4 knockdown was determined by transwell assays. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, NS: No significance. RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4.
- Citation: Chen PY, Wang PY, Liu B, Jia YP, Zhang ZX, Liu X, Wang DH, Yan YJ, Fu WH, Zhu F. RGS4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 100898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/100898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898