Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2025; 31(2): 100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
Published online Jan 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898
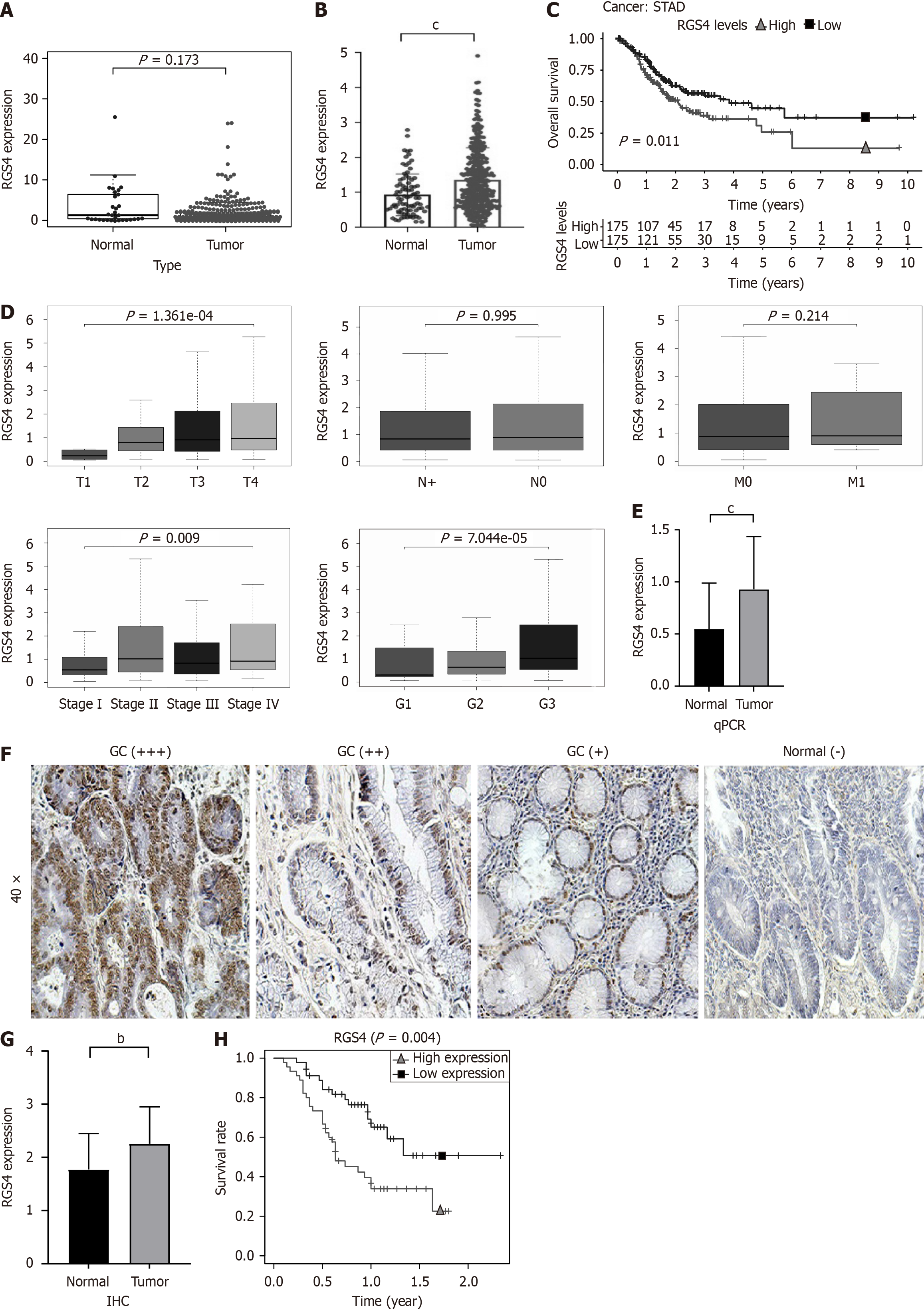
Figure 1 High expression of regulator of G protein signaling 4 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.
A: Differential expression of regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in The Cancer Genome Atlas Stomach Cancer dataset (TCGA-STAD); B: Differential expression of RGS4 in the integrated analysis of TCGA-STAD and the Genotype-Tissue Expression dataset; C: High expression of RGS4 was associated with lower overall survival in TCGA-STAD dataset; D: The correlation between RGS4 and T stage, N stage, M stage, tumor-node-metastasis stage and tumor grade of gastric cancer (GC); E: Differential expression of RGS4 in GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues of our center’s patients; F: Representative immunohistochemistry images showing the expression of RGS4 in GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues (strong staining: +++; moderate staining: ++; weak staining: +; negative staining: -); G: Differences in protein expression levels of RGS4 between GC and para-carcinoma normal tissues; H: High expression of RGS4 was associated with lower overall survival in GC patients in our center. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. RGS4: Regulator of G protein signaling 4; GC: Gastric cancer.
- Citation: Chen PY, Wang PY, Liu B, Jia YP, Zhang ZX, Liu X, Wang DH, Yan YJ, Fu WH, Zhu F. RGS4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through the focal adhesion kinase/phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(2): 100898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i2/100898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i2.100898