Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2025; 31(17): 105438
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438
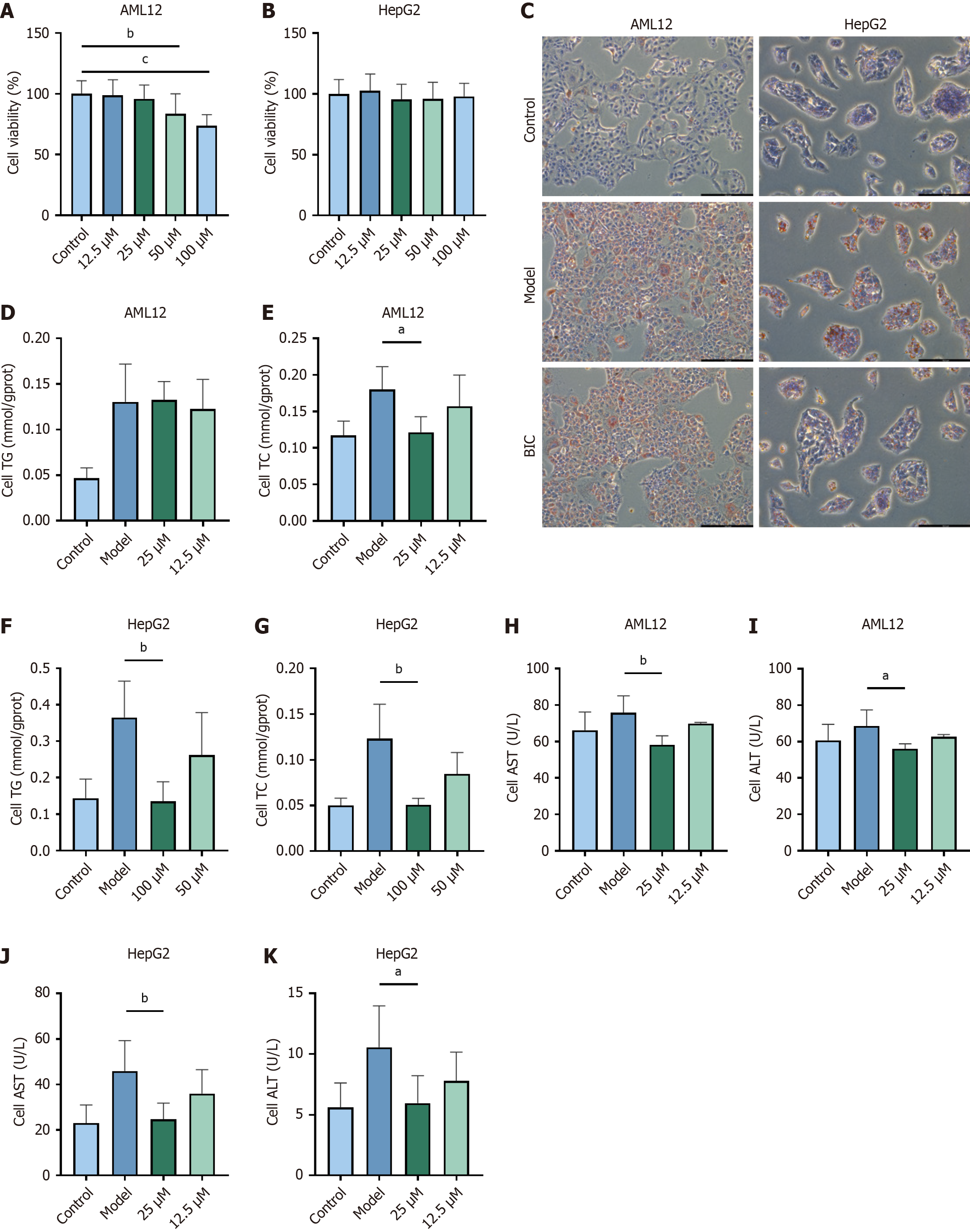
Figure 3 The therapeutic effect of bicuculline in a high-fat model of isolated hepatocytes.
A and B: Cytotoxic effects of different concentrations of bicuculline on AML12 cells and HepG2 cells; C: Oil red O staining results under light microscopy (200 ×); D-G: Relative total triglyceride and cholesterol levels in the two cell types; H-K: Absolute enzyme activity of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in the two cell types. The results are expressed as the means ± SDs (n = 5). Comparison between the treatment group and model group. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; TC: Total cholesterol; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TG: Triglyceride.
- Citation: Wang XM, Dai Z, Lu DJ, Bao CQ, Yang NB, Zhou YP. Bicuculline ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and reducing lipid accumulation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(17): 105438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i17/105438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438