Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2025; 31(17): 105438
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438
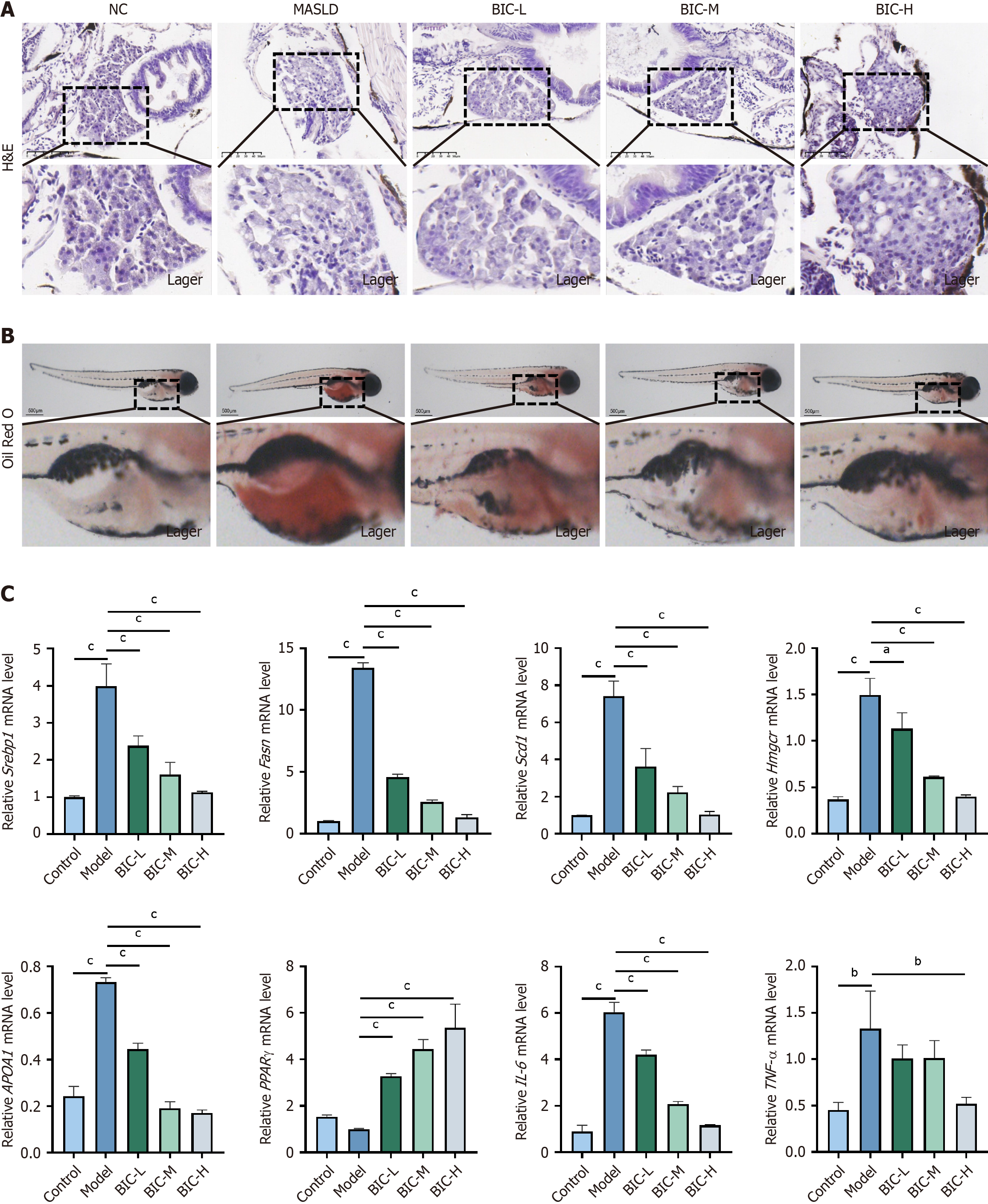
Figure 2 Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of bicuculline on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in zebrafish larvae.
A: Hematoxylin & eosin staining of the livers of zebrafish larvae in each group; B: Whole-fish oil red O staining; C: Effects of bicuculline on lipid metabolism-related genes and inflammatory factors. The results are expressed as the means ± SDs (n = 5). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test was used to compare all the groups. Compared with the model group, aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; BIC: Bicuculline; H&E: Hematoxylin & eosin; NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Wang XM, Dai Z, Lu DJ, Bao CQ, Yang NB, Zhou YP. Bicuculline ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and reducing lipid accumulation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(17): 105438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i17/105438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105438