Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2025; 31(17): 105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
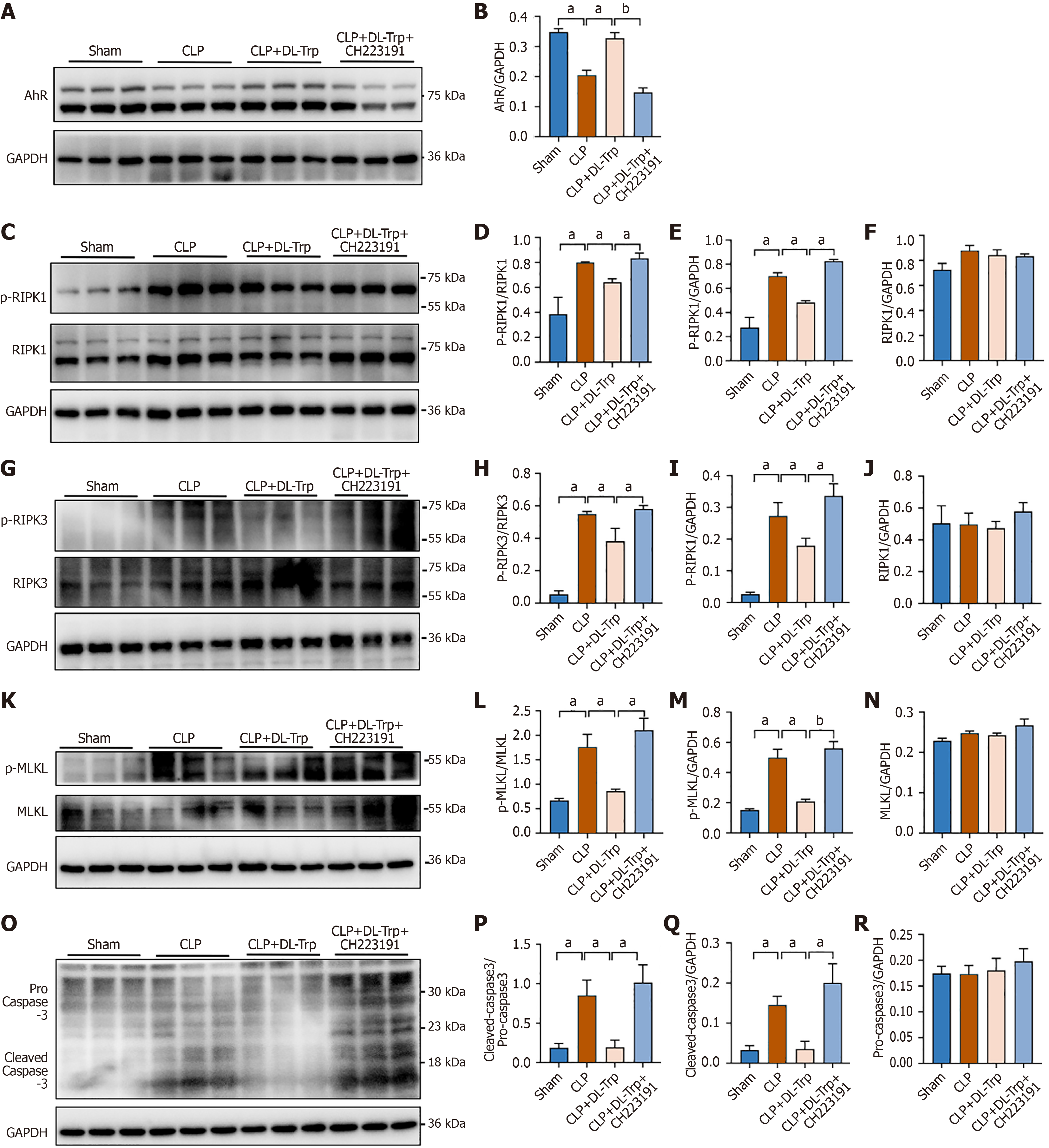
Figure 6 DL-tryptophan water inhibits necroptosis to mitigate sepsis-induced intestinal injury via aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
A and B: Western blotting of aryl hydrocarbon receptor; C-F: Western blotting of phospho-receptor-interacting protein kinase (p-RIPK) 1, receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK) 1; G-J: Western blotting of pRIPK3, RIPK3; K-N: Western blotting of phospho-mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; O-R: Western blotting of pro-caspase-3, and cleaved caspse-3 normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; DL-Trp: DL-tryptophan; AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; p-RIPK: Phospho-receptor-interacting protein kinase; RIPK: Receptor-interacting protein kinase; MLKL: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; p-MLKL: Phospho-mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein.
- Citation: Wang Q, Liu CZ, Li BT, Yu XQ, Zhang JY, Wang ZT, Liao LJ, Liu XD. Ozone controls the metabolism of tryptophan protecting against sepsis-induced intestinal damage by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(17): 105411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i17/105411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411