Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2025; 31(17): 105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
Published online May 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411
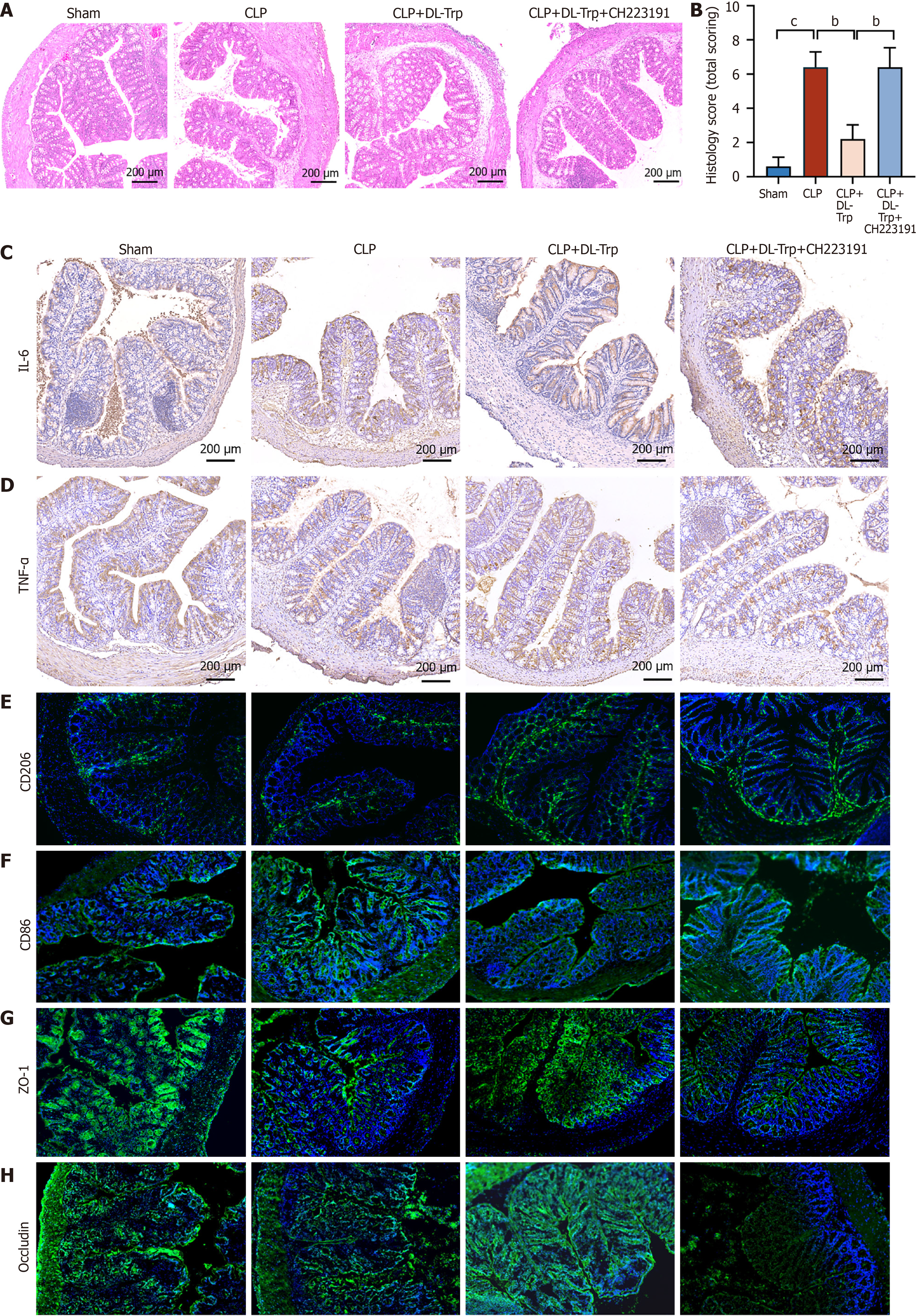
Figure 5 Tryptophan metabolism of the intestinal flora-DL-tryptophan activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor to mitigate sepsis-induced intestinal injury.
A and B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining; C and D: Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in the colon, shown by immunohistochemistry; E-H: Immunofluorescence staining of cluster of differentiation (CD) 206, CD86, zonula occludens-1, and occluding. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. CLP: Cecal ligation and puncture; DL-Trp: DL-tryptophan; IL-6: Interleukin-6; CD: Cluster of differentiation; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1.
- Citation: Wang Q, Liu CZ, Li BT, Yu XQ, Zhang JY, Wang ZT, Liao LJ, Liu XD. Ozone controls the metabolism of tryptophan protecting against sepsis-induced intestinal damage by activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(17): 105411
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i17/105411.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i17.105411