Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 105985
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105985
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105985
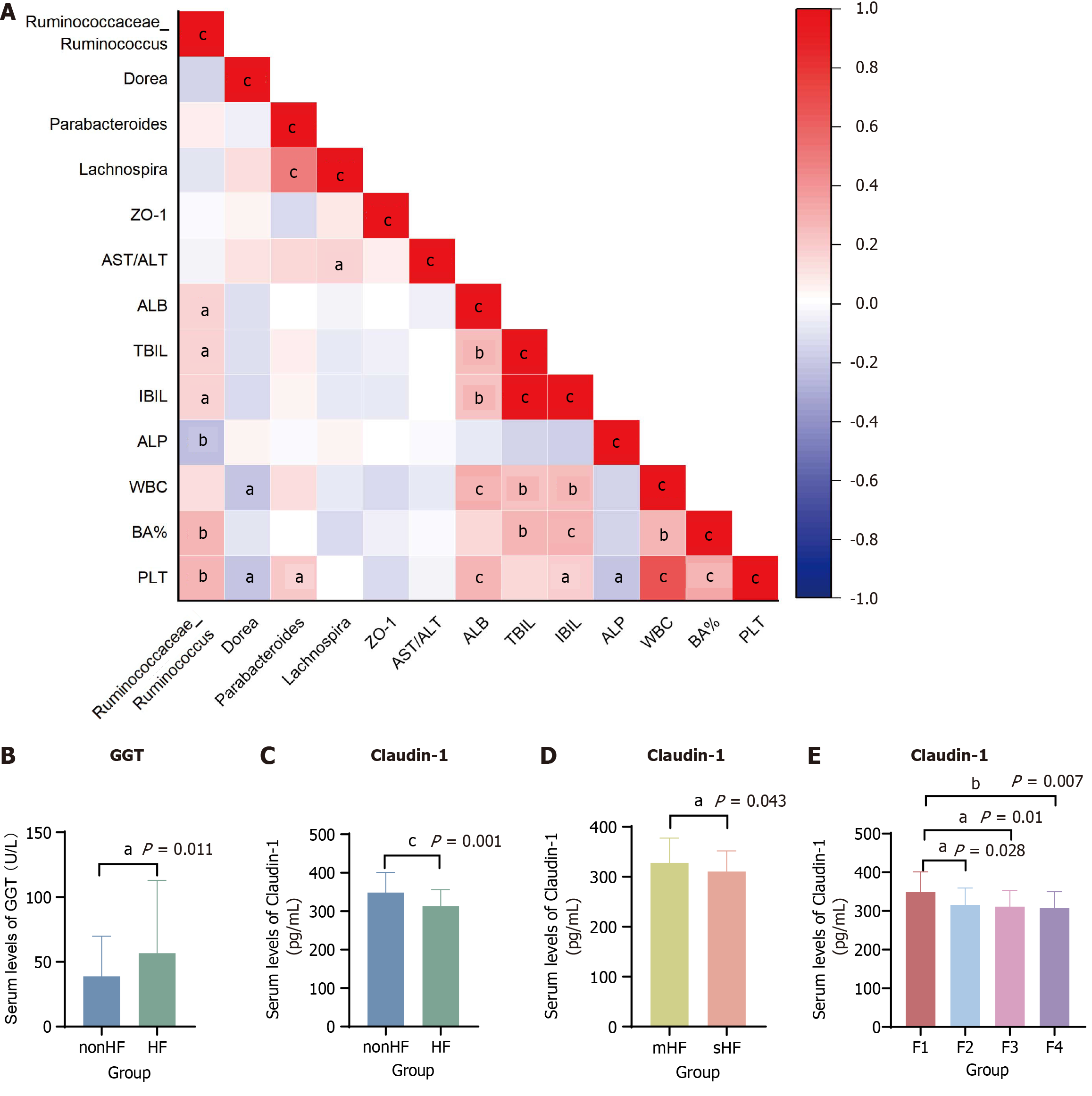
Figure 5 The relationship between gut microbiota, clinical indicators, and intestinal barrier function in different stages of hepatic fibrosis patients.
A: The correlation analyses among gut microbiota, clinical indicators, and intestinal barrier function in hepatic fibrosis (HF) patients; B: The serum levels of γ-glutamyl transferase in different stages of HF patients; C-E: The serum levels of intestinal barrier function in different stages of HF patients. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; ALB: Albumin; TBIL: Total bilirubin; IBIL: Indirect bilirubin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; WBC: White blood cell; BA: Basophil; PLT: Platelet; GGT: γ-glutamyl transferase; HF: Hepatic fibrosis; mHF: Mild hepatic fibrosis; sHF: Significant hepatic fibrosis.
- Citation: Zhu Y, Geng SY, Chen Y, Ru QJ, Zheng Y, Jiang N, Zhu FY, Zhang YS. Machine learning algorithms reveal gut microbiota signatures associated with chronic hepatitis B-related hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 105985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/105985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105985