Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 105188
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188
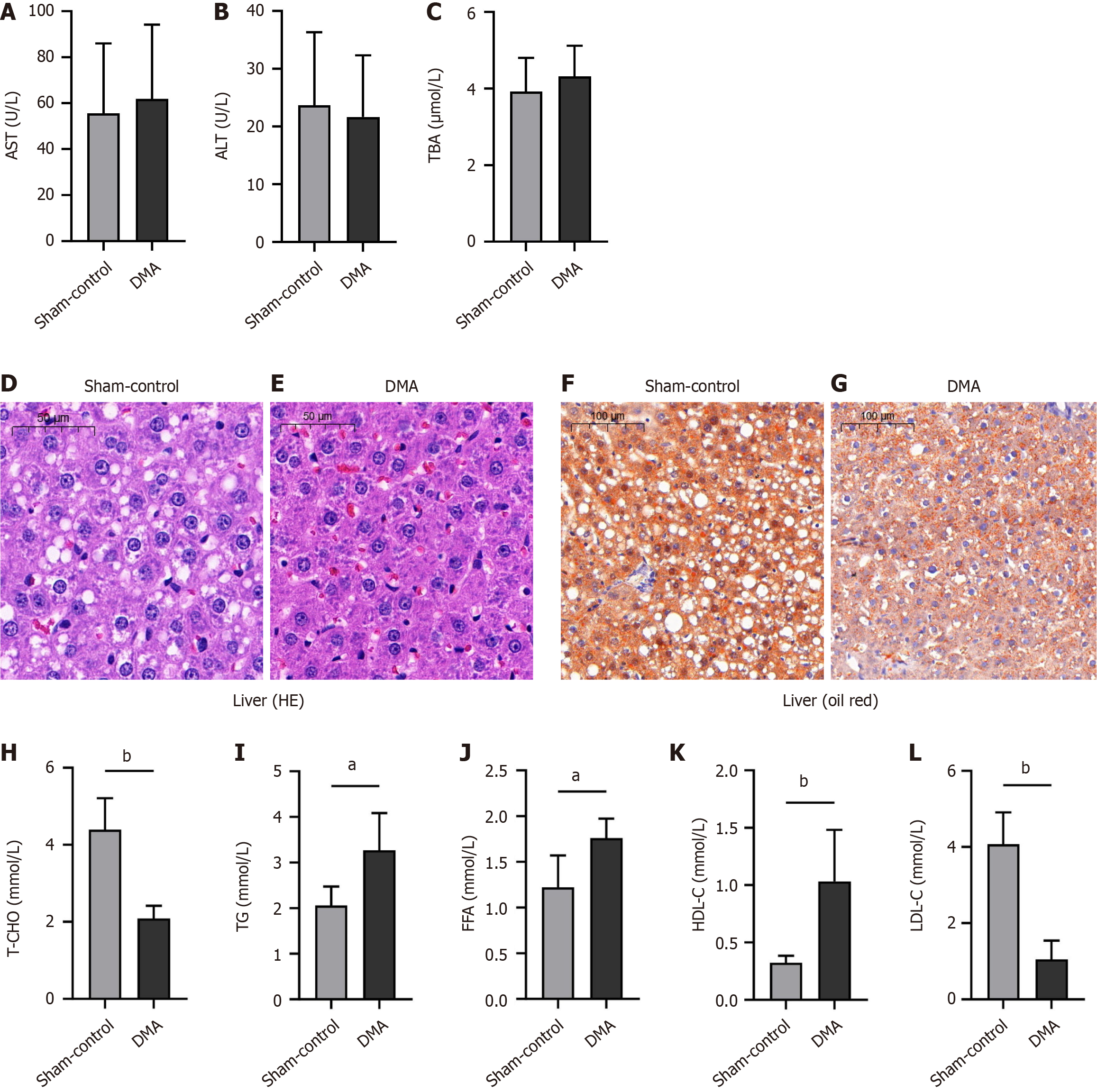
Figure 5 Liver function parameter test, histological examination, and serum lipid parameter test among different groups.
A: Serum aspartate aminotransferase levels; B: Alanine aminotransferase; C: Total bile acids; D-G: Histological examination of the liver tissue via hematoxylin and eosin staining and oil red O staining from the sham-control group and from the duodenal mucosal ablation group; H-L: Serum total cholesterol, triacylglycerol, free fatty acid, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs sham-control group, bP < 0.01 vs sham-control group. DMA: Duodenal mucosal ablation; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; TBA: Total bile acid; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; T-CHO: Total cholesterol; TG: Triacylglycerol; FFA: Free fatty acid; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
- Citation: Yu JW, Zhao Q, Li PX, Zhang YX, Gao BX, Xiang LB, Liu XY, Wang L, Sun YJ, Yang ZZ, Shi YJ, Chen YF, Yu MB, Zhang HK, Zhang L, Xu QH, Ren L, Li D, Lyu Y, Ren FG, Lu Q. Duodenal mucosal ablation with irreversible electroporation reduces liver lipids in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 105188
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/105188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188