Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 105188
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188
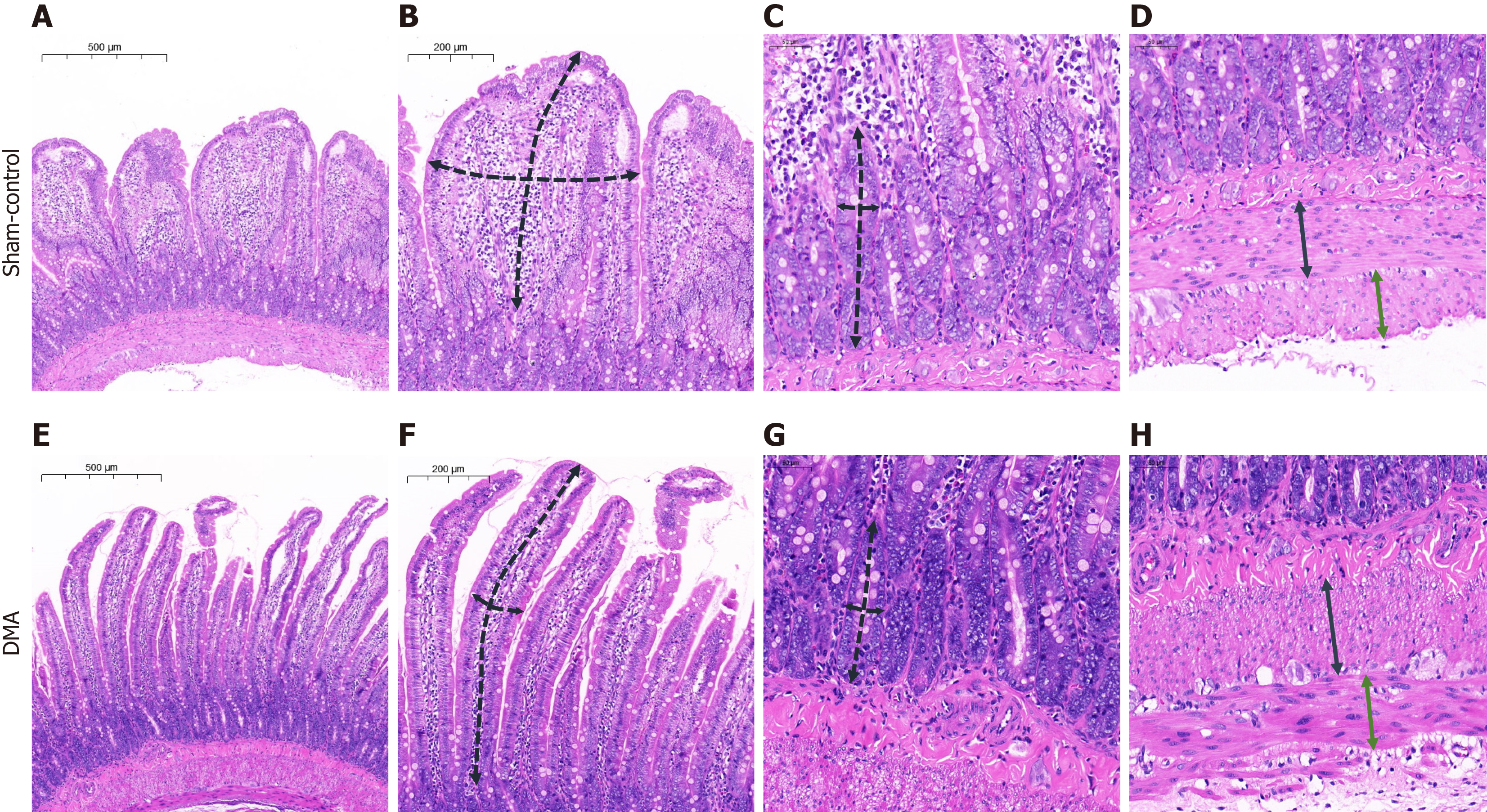
Figure 4 Histological examination of the duodenal tissue.
A: Complete layer of the duodenal wall, sham-control group; B: Measurement scheme of the length (a long dashed black line) and thickness (a short dashed black line) of the villus, sham-control group; C: Measurement scheme of the depth (a long dashed black line) and thickness (a short dashed black line) of the crypt, sham-control group; D: Measurement scheme of the longitudinal (a continuous black line) and circular (a continuous green line) lamina, sham-control group; E: Complete layer of the duodenal wall, duodenal mucosal ablation group; F: Measurement scheme of the length (a long dashed black line) and thickness (a short dashed black line) of the villus, duodenal mucosal ablation group; G: Measurement scheme of the depth (a long dashed black line) and thickness (a short dashed black line) of the crypt, duodenal mucosal ablation group; H: Measurement scheme of the longitudinal (a continuous black line) and circular (a continuous green line) lamina, duodenal mucosal ablation group. DMA: Duodenal mucosal ablation.
- Citation: Yu JW, Zhao Q, Li PX, Zhang YX, Gao BX, Xiang LB, Liu XY, Wang L, Sun YJ, Yang ZZ, Shi YJ, Chen YF, Yu MB, Zhang HK, Zhang L, Xu QH, Ren L, Li D, Lyu Y, Ren FG, Lu Q. Duodenal mucosal ablation with irreversible electroporation reduces liver lipids in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 105188
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/105188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105188