Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
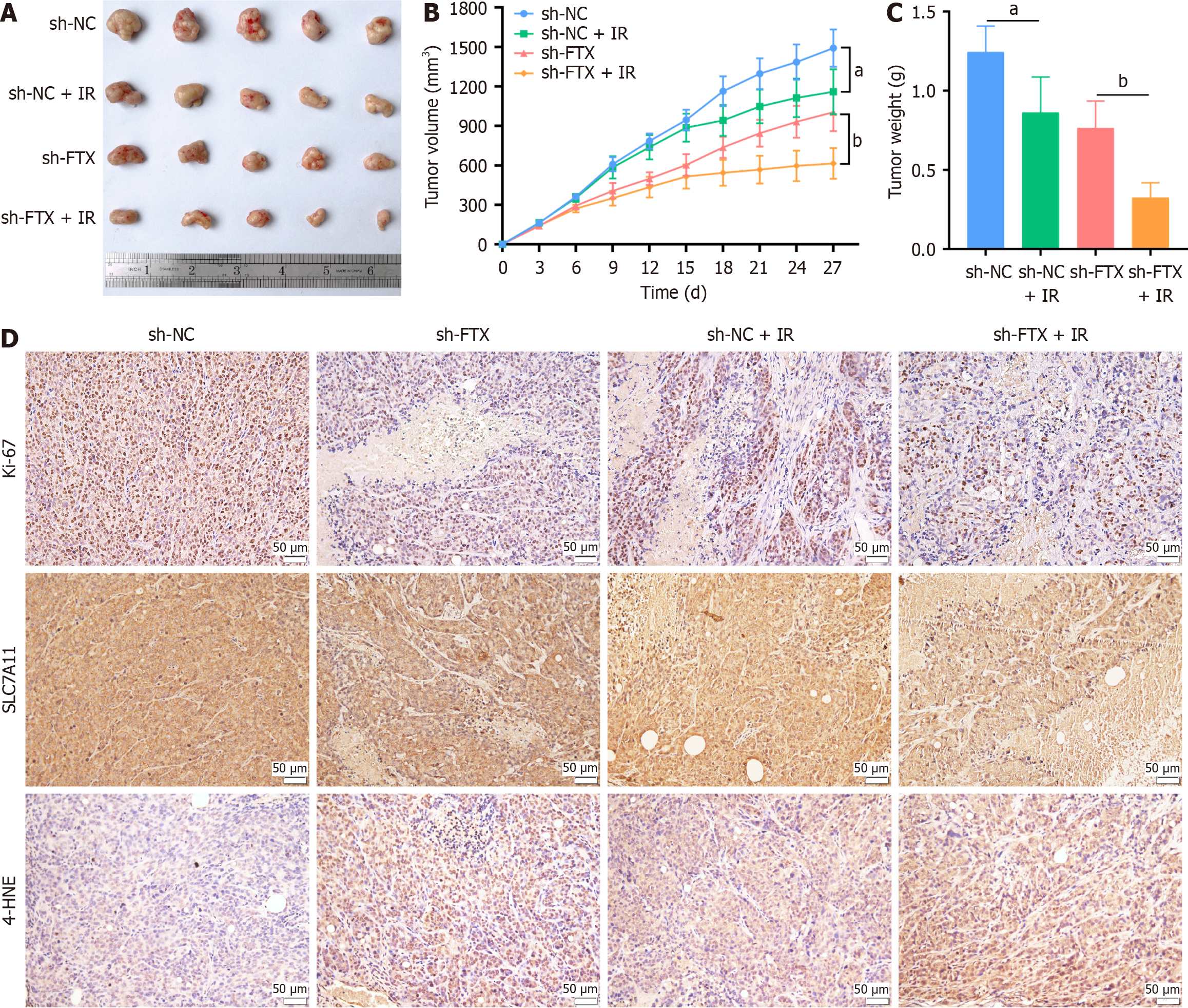
Figure 7 Inhibition of lncRNA FTX increases the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer in vivo.
A: Representative images of the tumors after receiving or not by 10 Gy irradiation, formed by HT29R-sh-FTX or control cells subcutaneous vaccination; B: Tumor volume in xenograft mice of each group at the indicated times; C: Tumor weights of xenograft mice from each group; D: Representative immunohistochemical staining images of Ki-67, SLC7A11, and 4-HNE in the subcutaneous tumor xenograft tissues. Scale bar: 50 μm. Data are expressed mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control; IR: Ionizing radiation.
- Citation: Dai Q, Qu TY, Yang JL, Leng J, Fang L, Zhu QQ, Wu KB, Wu J, Ma JJ, Yu HF. LncRNA FTX promotes colorectal cancer radioresistance through disturbing redox balance and inhibiting ferroptosis via miR-625-5p/SCL7A11 axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 104305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/104305.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305