Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305
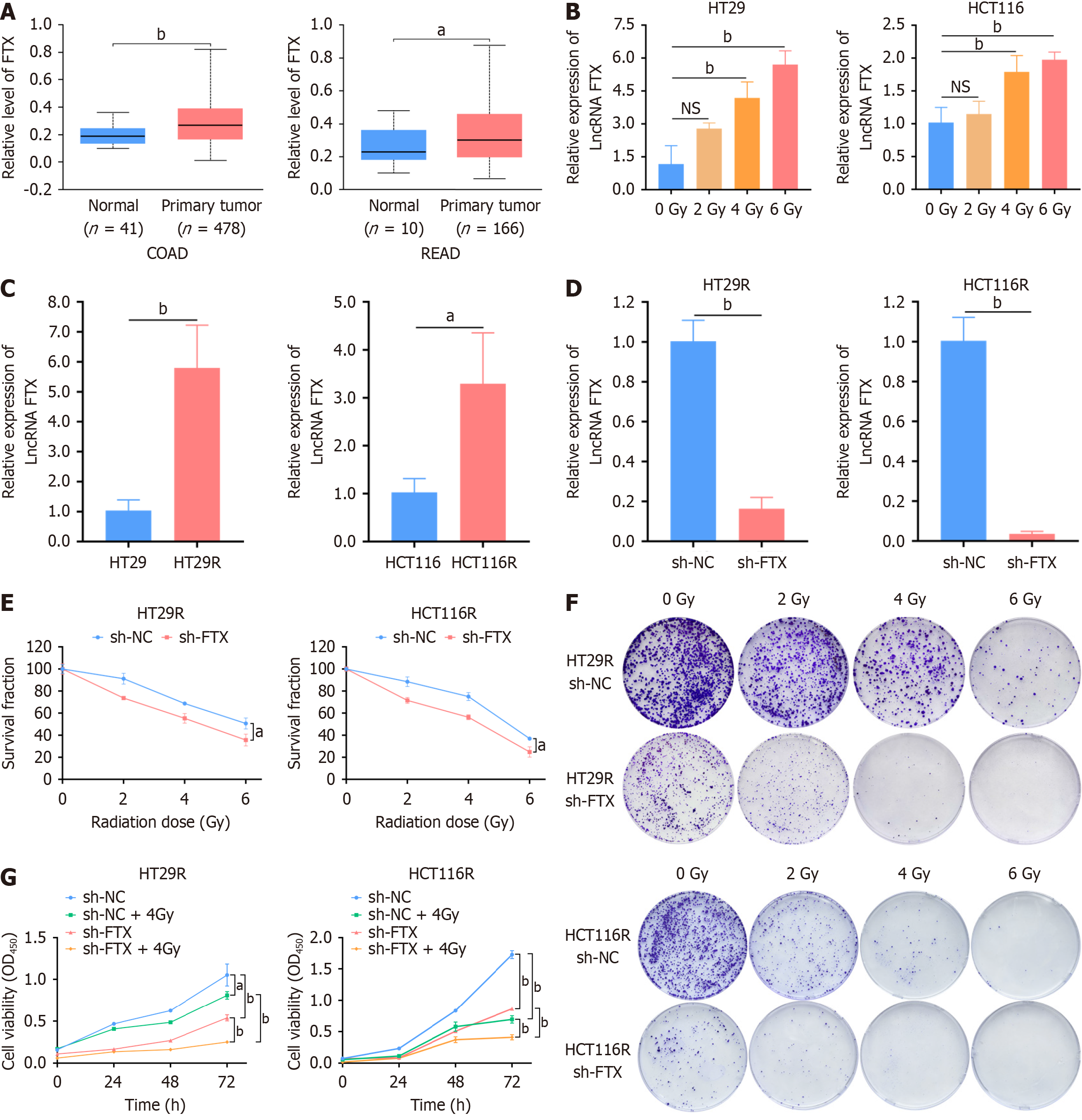
Figure 1 LncRNA FTX is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells and associated with the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer.
A: lncRNA FTX expression in colon, rectal cancer, and para-cancerous tissues; B: Relative expression of lncRNA FTX in HT29 and HCT116 cells after irradiation at different doses; C: LncRNA FTX expression was significantly higher in colorectal cancer radiotherapy-resistant cells than in the corresponding parental cells; D: Knockdown efficiency of lncRNA FTX in HT29R and HCT116R cells was validated by real-time quantitative PCR; E: Knockdown of FTX expression in HT29R and HCT116R markedly increased the sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy; F: Colony formation assay revealed that knockdown of FTX significantly increased the sensitivity of HT29R and HCT116R cells to radiotherapy; G: Cell viability was determined using CCK-8 assay after transfection of sh-FTX and sh-negative control in HT29R or HCT116R cells, which were irradiated by 4 Gy. All representative data are from three independent experiments, and the results are presented as deviation mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was conducted using the student's t-test. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01. NC: Negative control.
- Citation: Dai Q, Qu TY, Yang JL, Leng J, Fang L, Zhu QQ, Wu KB, Wu J, Ma JJ, Yu HF. LncRNA FTX promotes colorectal cancer radioresistance through disturbing redox balance and inhibiting ferroptosis via miR-625-5p/SCL7A11 axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 104305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/104305.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.104305