Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2025; 31(15): 105720
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.105720
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.105720
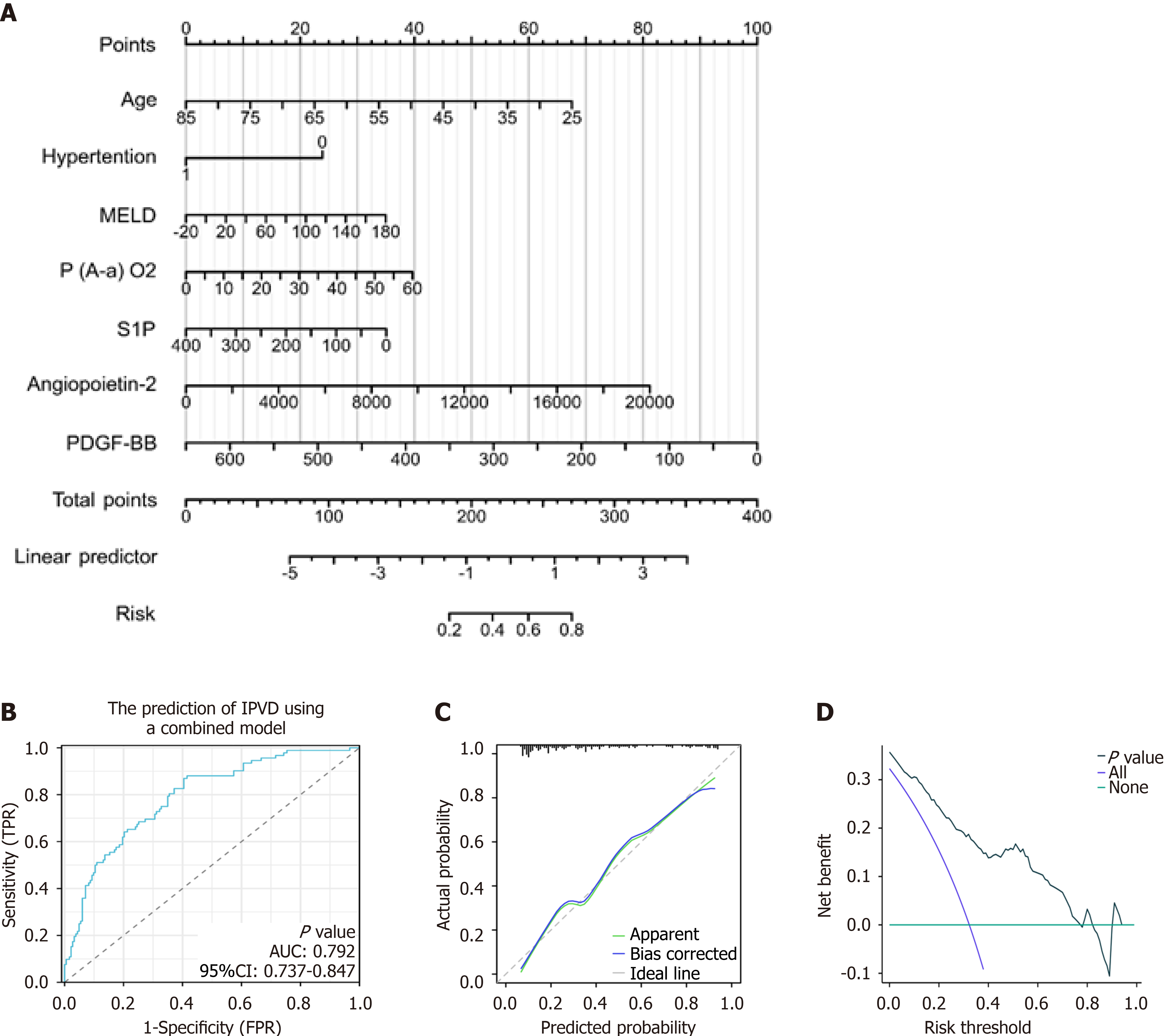
Figure 5 Predictive model for intrapulmonary vascular dilatation combining clinical parameters and biomarkers.
A: Nomogram of the predictive model for intrapulmonary vascular dilatation (IPVD) in patients with cirrhosis. This model integrates four clinical parameters and three biomarkers; B: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve predicting IPVD in patients with cirrhosis. Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.792 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.737-0.847); C: Calibration curves; D: Decision curve analysis of the nomogram for the prediction of IPVD. FPR: False-positive rate; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; P(A-a)O2: Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient; PDGF-BB: Platelet-derived growth factor BB; S1P: Sphingosine 1 phosphate; TPR: True-positive rate.
- Citation: Wu ZP, Wang YF, Shi FW, Cao WH, Sun J, Yang L, Ding FP, Hu CX, Kang WW, Han J, Yang RH, Song QK, Jin JW, Shi HB, Ma YM. Predictive models and clinical manifestations of intrapulmonary vascular dilatation and hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with cirrhosis: Prospective comparative study. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(15): 105720
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i15/105720.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.105720