Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2025; 31(15): 104996
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104996
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104996
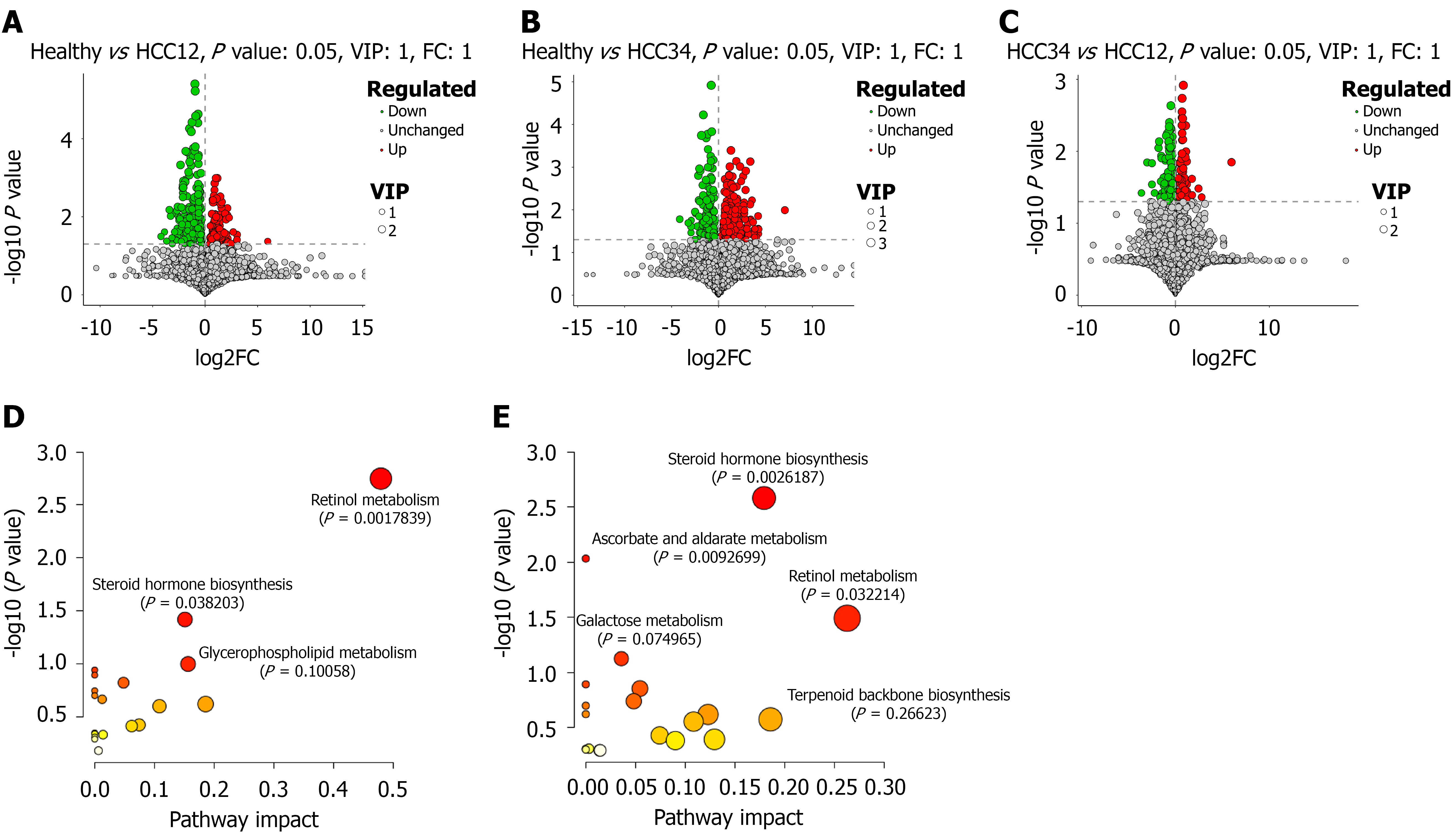
Figure 2 Volcano plots of the differential metabolites and bubble plots of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways.
A-C: The differential metabolites of healthy control (HC) vs comprising patients with stage I and II hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC12) (A), HC vs comprising patients with stage III and IV hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC34) (B), and HCC12 vs HCC34 (C) were displayed as volcano plots; D and E: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis was separately performed on the MetaboAnalyst website (https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/) for the differential metabolites in the two comparisons, namely HC vs HCC12 (D) and HC vs HCC34 (E). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HCC12: Comprising patients with stage I and II hepatocellular carcinoma; HCC34: Comprising patients with stage III and IV hepatocellular carcinoma; VIP: Variable importance in projection; FC: Fold change.
- Citation: Feng J, Wang JP, Hu JR, Li P, Lv P, He HC, Cheng XW, Cao Z, Han JJ, Wang Q, Su Q, Liu LX. Multi-omics reveals the associations among the fecal metabolome, intestinal bacteria, and serum indicators in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(15): 104996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i15/104996.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104996