Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2025; 31(15): 101058
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.101058
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.101058
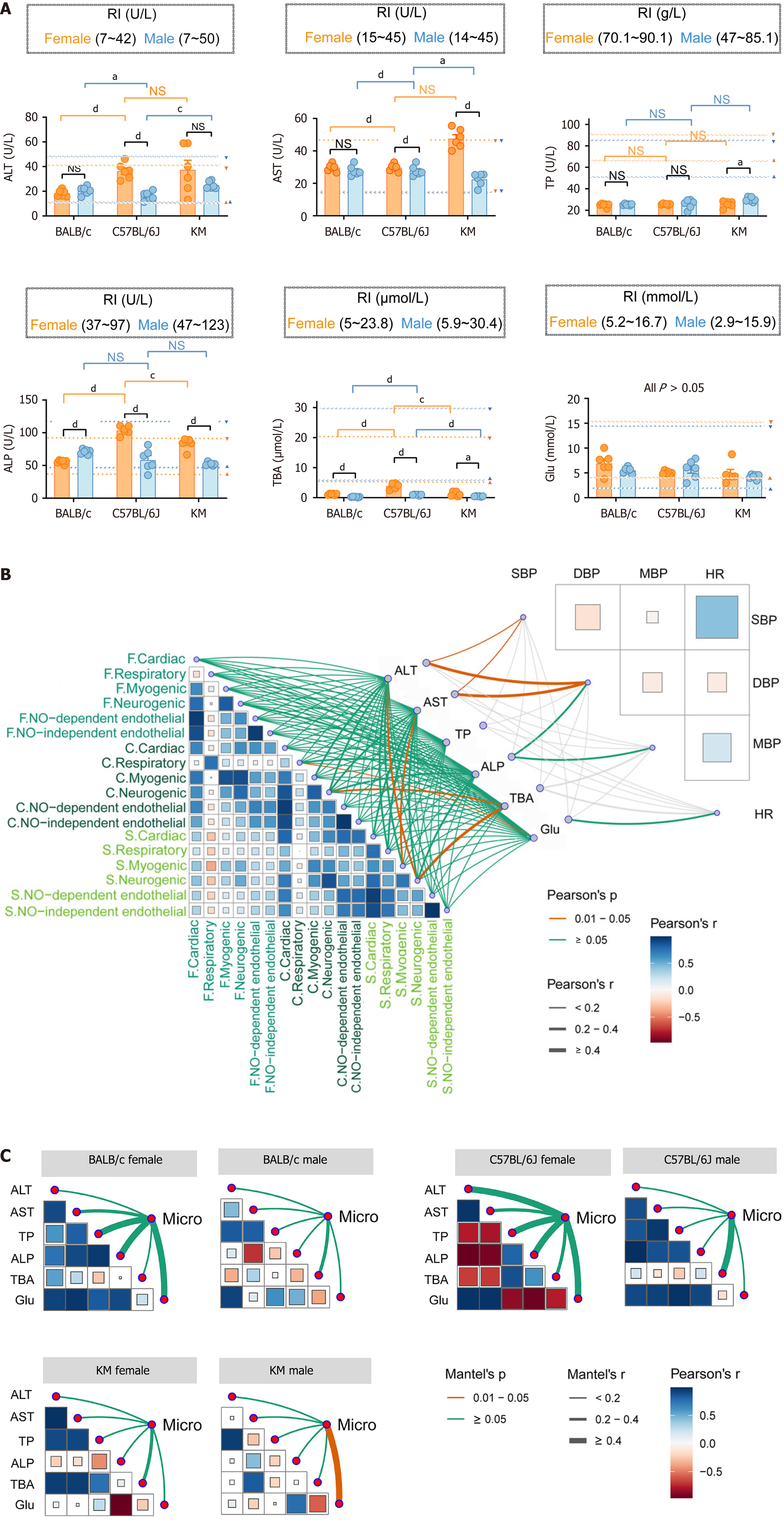
Figure 5 Relationship among hepatic microhemodynamics, liver function and macrohemodynamics.
A: Cross-comparison of liver function between different mouse strains and sexes. The established reference values for each of the five indicators are marked with dashed lines, with triangles serving as indicating markers. Yellow represents females, whereas blue signifies males; B: Interrelationships among the mean amplitudes of the three microhemodynamic indicators and macrohemodynamic indicators were analyzed using Pearson correlation analysis. The correlations among liver function indicators, hepatic microhemodynamics, and blood pressure and heart rate were shown respectively with connecting lines indicating these relationships. Microhemodynamics indicators: Flux, concentration, and speed; Liver function indicators: Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total protein, alkaline phosphatase, total bile acid, and glucose; Macrohemodynamics indicators: Heart rate, systolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and diastolic blood pressure. P values are represented by the color, and r values are represented by the line thickness; C: The relationships between microhemodynamics and liver function, across different mouse strains and between sexes, were independently analyzed using the Mantel test (n = 6 each group). The edge width signifies the correlation strength, while the edge color indicates statistical significance. “Micro” indicates the mean amplitude of the five characteristic frequencies of flux, concentration, and speed. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n = 6 each group. aP < 0.05. cP < 0.001. dP < 0.0001. RI: Respiratory index; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TP: Total protein; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; TBA: Total bile acid; Glu: Glucose; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; HR: Heart rate; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; MBP: Mean arterial pressure.
- Citation: Wang B, Li Y, Ouyang Q, Xu MT, Wang YY, Fu SJ, Liu WQ, Liu XT, Ling H, Zhang X, Xiu RJ, Liu MM. Strain- and sex-dependent variability in hepatic microcirculation and liver function in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(15): 101058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i15/101058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.101058