Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2025; 31(14): 104117
Published online Apr 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104117
Published online Apr 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104117
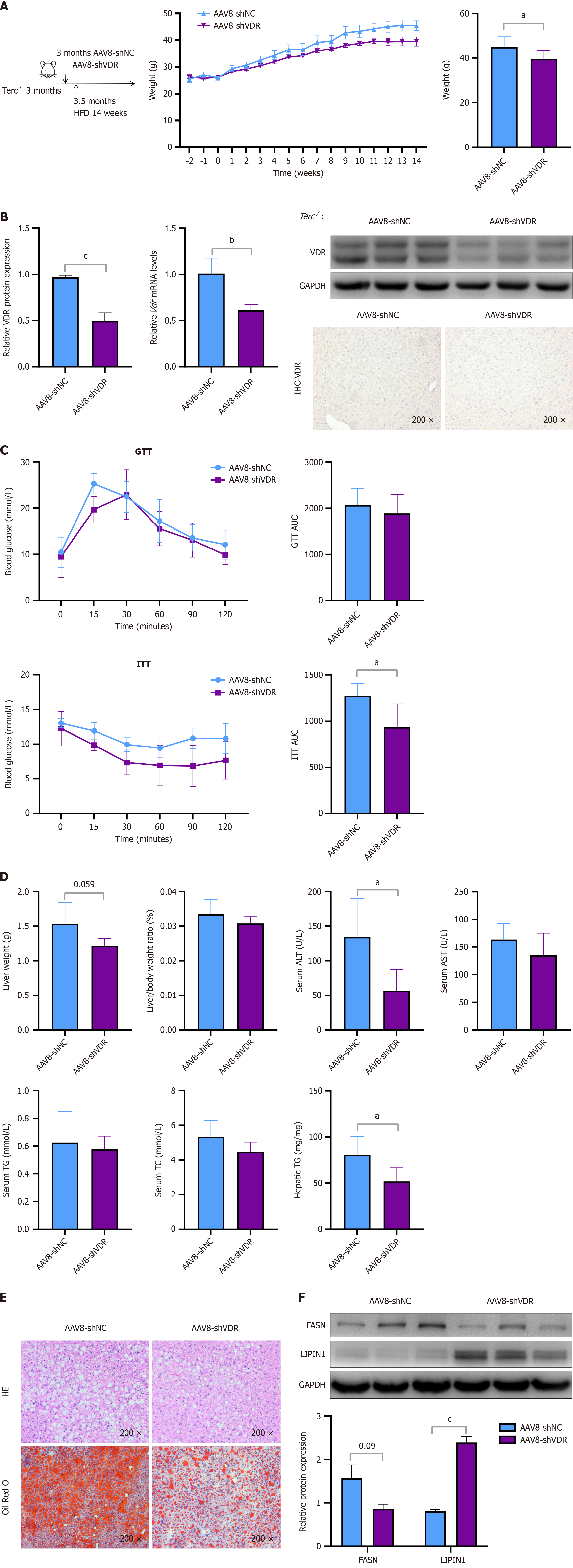
Figure 6 The hepatic-specific downregulation of vitamin D receptor ameliorated hepatic steatosis in telomerase RNA component knockout mice mice.
Telomerase RNA component knockout mice were injected with adeno-associated virus 8 (AAV8)-short hairpin (sh)-negative control (NC) or AAV8-sh-vitamin D receptor (VDR) at 3 months of age. Two weeks after the injection, these mice were fed a high-fat diet for 14 weeks. A: Weights and changes in weight; B: The protein expression level of VDR and corresponding quantitative results, the mRNA level of VDR, and immunohistochemical staining (× 200) for VDR in liver sections; C: Glucose tolerance test and associated area under the curve (AUC). Insulin tolerance test and associated AUC; D: Liver weights, liver-to-body weight ratio, serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, triglycerides (TGs), and total cholesterol, and hepatic levels of TGs; E: Hematoxylin-eosin and Oil Red O staining (× 200) of the liver sections; F: The protein expression levels of FASN and LIPIN1 and corresponding quantitative results. Protein levels and mRNA levels were normalized to those of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The data are presented as the means ± SDs. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. P calculated according to student’s t tests. AAV8: Adeno-associated virus 8; shNC: Short hairpin-negative control; shVDR: Short hairpin vitamin D receptor; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin; VDR: Vitamin D receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GTT: Glucose tolerance test; ITT: Insulin tolerance test; AUC: Area under the curve; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TG: Triglycerides; TC: Total cholesterol.
- Citation: Zhu F, Lin BR, Lin SH, Yu CH, Yang YM. Hepatic-specific vitamin D receptor downregulation alleviates aging-related metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(14): 104117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i14/104117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i14.104117