Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2025; 31(13): 104697
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104697
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104697
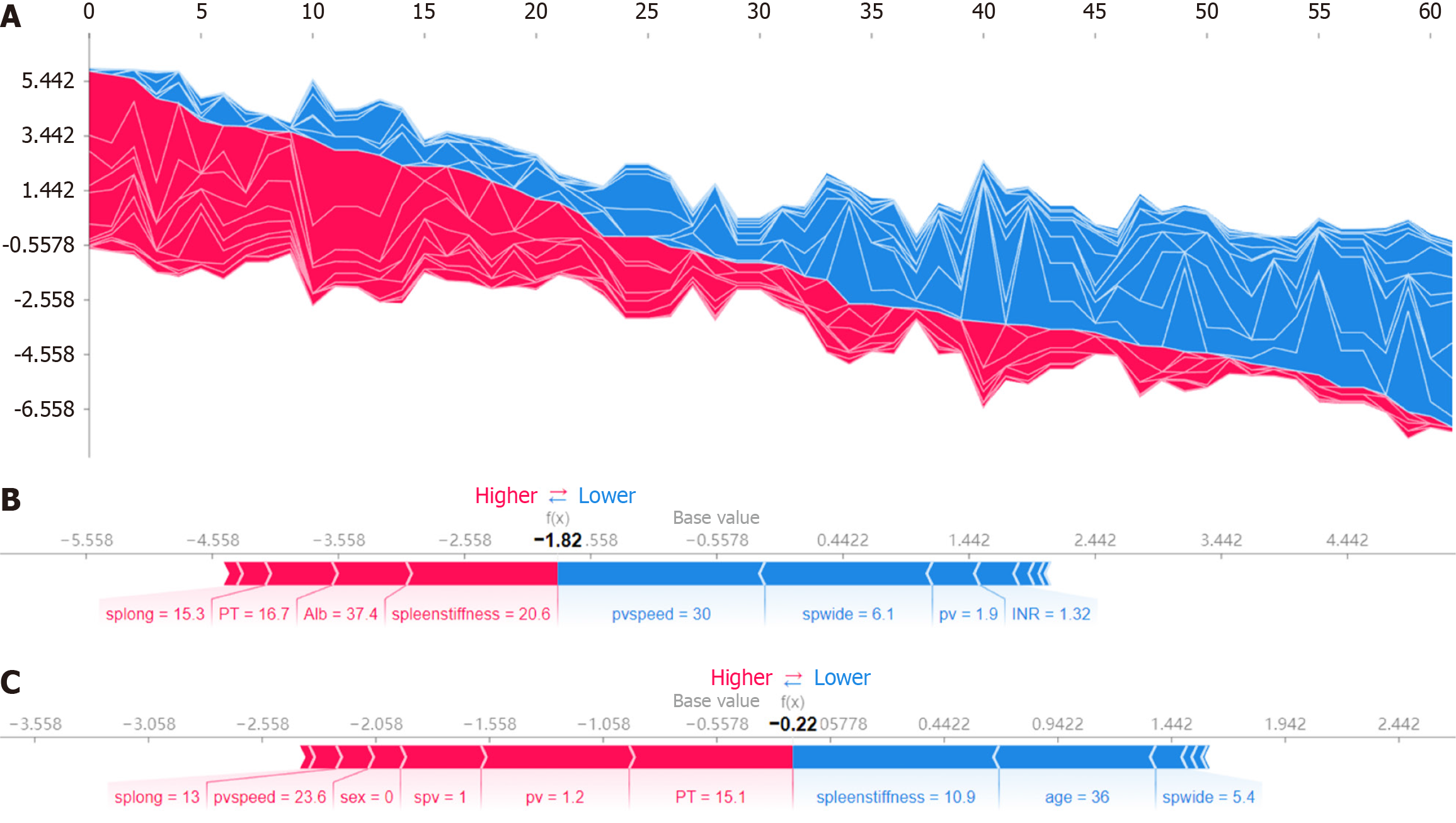
Figure 5 SHapley Additive exPlanation force plots demonstrating model predictions for actual patients.
A: The force plot for all patients illustrates the SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) values, showing how each feature contributes to the predictions of the model for each individual. The x-axis represents the model output value, with red indicating an increase in the prediction score (higher risk) and blue indicating a decrease (lower risk). This comprehensive view demonstrates the impact of features like portal vein speed, spleen width and spleen stiffness on the predictions for all patients; B: The force plot application for actual patients further interprets model predictions. The force plot for inaccurately predicted patients displays the SHAP values for a case where the model prediction was incorrect. Features such as spleen length, prothrombin time and albumin are highlighted, showing their contributions to the incorrect prediction. Red bars indicate features that increased the prediction score, leading to a higher risk, while blue bars indicate features that decreased the score, indicating a lower risk; C: The force plot for accurately predicted patients shows the SHAP values for a correctly predicted case. Significant features like spleen stiffness, age and spleen width are shown with their respective contributions, demonstrating how these features combined to provide an accurate risk assessment, with red bars increasing the prediction score and blue bars decreasing it. splong: Spleen length; PT: Prothrombin time; Alb: Albumin; pvspeed: Portal vein speed; pv: Portal vein; spwide: Spleen width; INR: International normalized ratio.
- Citation: Feng SY, Ding ZR, Cheng J, Tu HB. Noninvasive prediction of esophagogastric varices in hepatitis B: An extreme gradient boosting model based on ultrasound and serology. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(13): 104697
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i13/104697.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104697