Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2025; 31(13): 104671
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104671
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104671
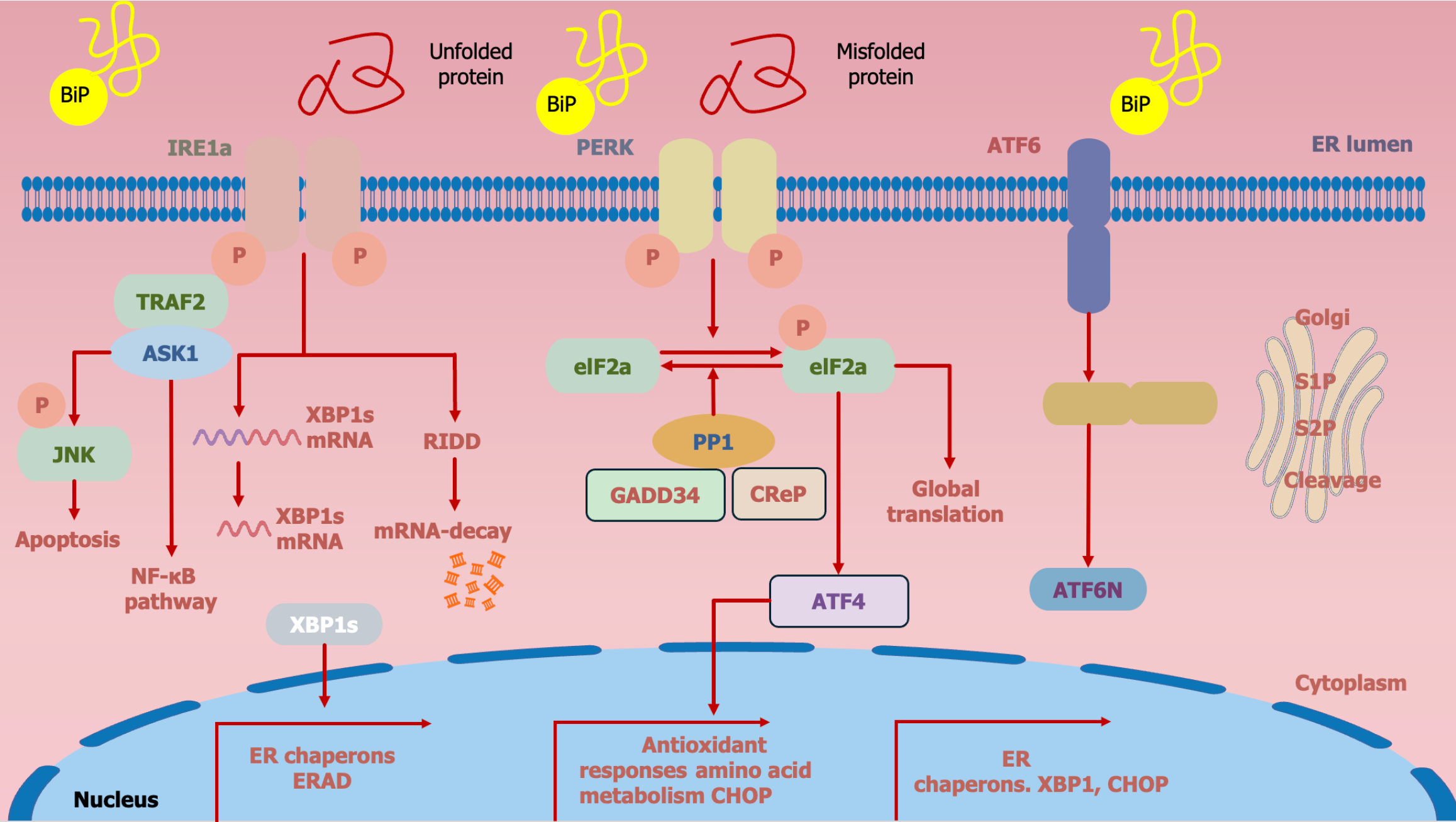
Figure 3 Unfolded protein response pathways in endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress is triggered when protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum goes awry and unfolded or misfolded proteins aggregate abnormally in the endoplasmic reticulum, followed by unfolded protein response to correct the situation, including inositol-requiring enzyme 1, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase, and activating transcription factor 6. IRE1: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1; PERK: Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; TRAF2: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2; ASK1: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; RIDD: Regulated inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha-dependent decay; ERAD: Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.
- Citation: Zheng T, Huang KY, Tang XD, Wang FY, Lv L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in gut inflammation: Implications for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(13): 104671
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i13/104671.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104671