Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2025; 31(13): 104370
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104370
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104370
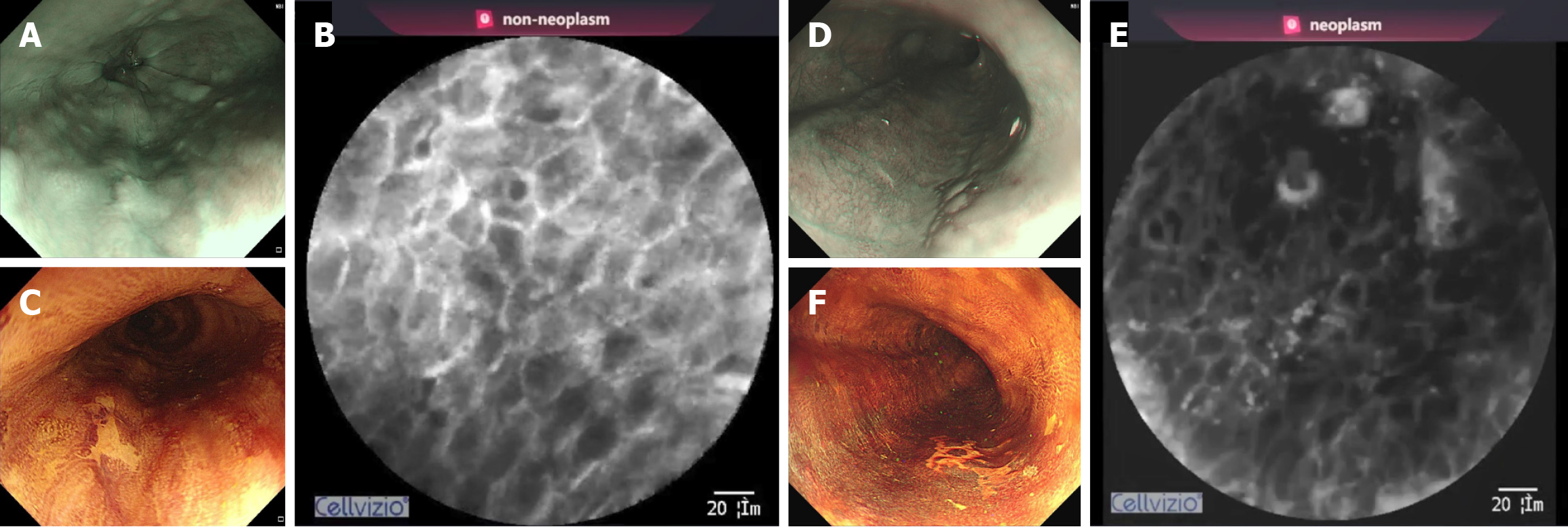
Figure 3 Diagnosis of intelligent confocal laser endomicroscopy for esophageal lesions.
A: A brownish lesion observed on narrow-band imaging (NBI); B: Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) image of inflammatory epithelium; Intelligent confocal laser endomicroscopy (iCLE) shows the diagnosis of non-neoplasm; C: The lesion shows Lugol-voiding on Lugol’s iodine chromoendoscopy (LCE) after the pCLE procedure; D: Another brownish lesion observed on NBI; E: PCLE image of esophageal squamous neoplasms with the squamous maturation score was 0; ICLE shows the diagnosis of neoplasm; F: Lugol-voiding observed on LCE.
- Citation: Ma T, Liu GQ, Guo J, Ji R, Shao XJ, Li YQ, Li Z, Zuo XL. Artificial intelligence-aided optical biopsy improves the diagnosis of esophageal squamous neoplasm. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(13): 104370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i13/104370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.104370