Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2025; 31(13): 100863
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100863
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100863
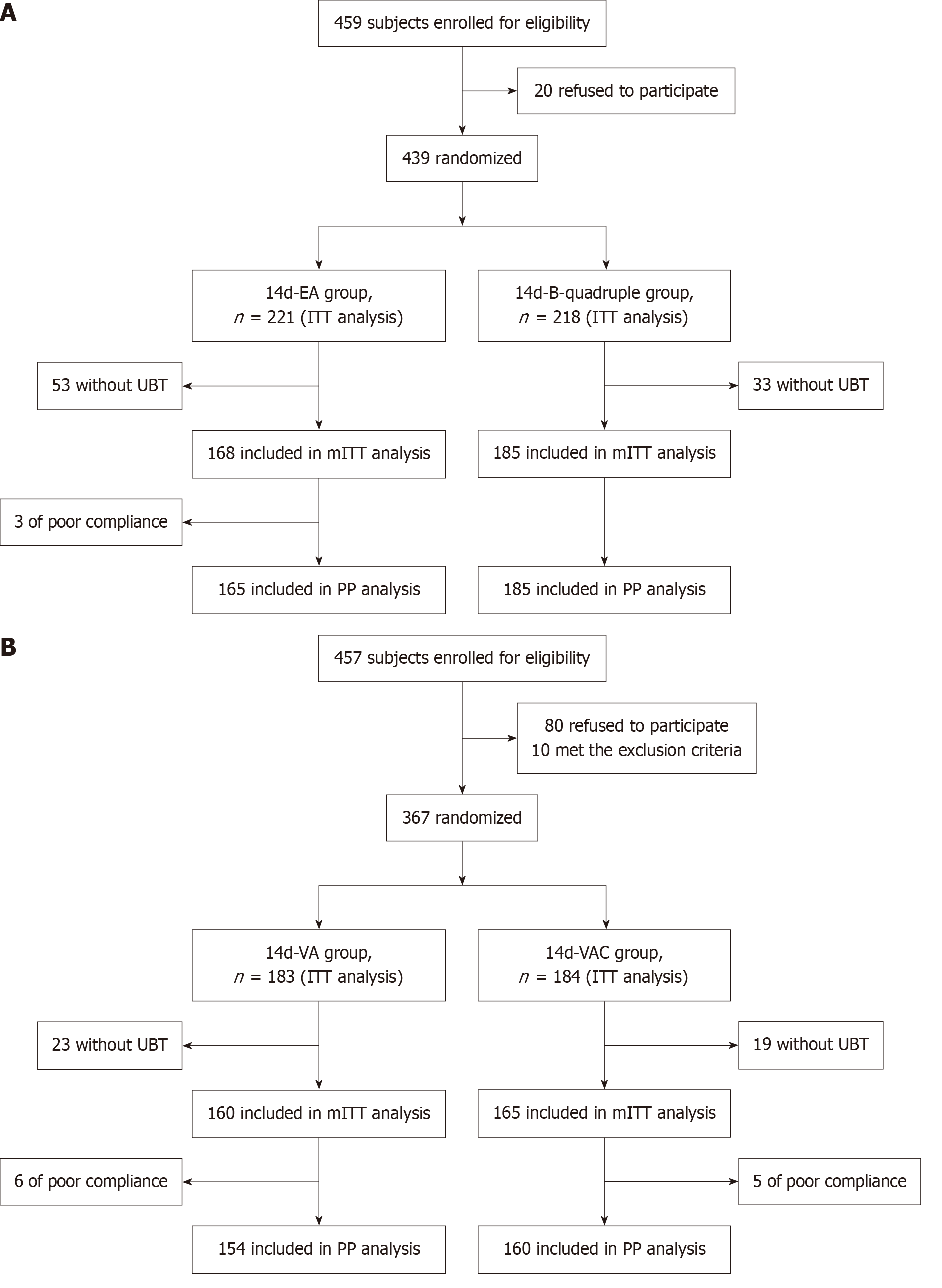
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient recruitment.
A: The study of 14-day esomeprazole and amoxicillin high-dose dual therapy and 14-day bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (14-day esomeprazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and bismuth therapy); B: The study of 14-day vonoprazan and amoxicillin high-dose dual therapy and 14-day vonoprazan, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin therapy. ITT: Intention-to-treat; mITT: Modified intention-to-treat; PP: Per-protocol; UBT: Urea breath test; EA: Esomeprazole-amoxicillin; B-quadruple: Esomeprazole-amoxicillin-clarithromycin-bismuth; VA: Vonoprazan-amoxicillin; VAC: Vonoprazan-amoxicillin-clarithromycin.
- Citation: Yang XE, Zhang SJ, Liu Y, Yao SY, Zhang SX, Liu XM, Liang LX, Wang F. Amoxicillin high-dose dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori primary eradication: Proton pump inhibitor and potassium-competitive acid blocker, which’s better? World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(13): 100863
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i13/100863.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100863