Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2025; 31(13): 100566
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100566
Published online Apr 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100566
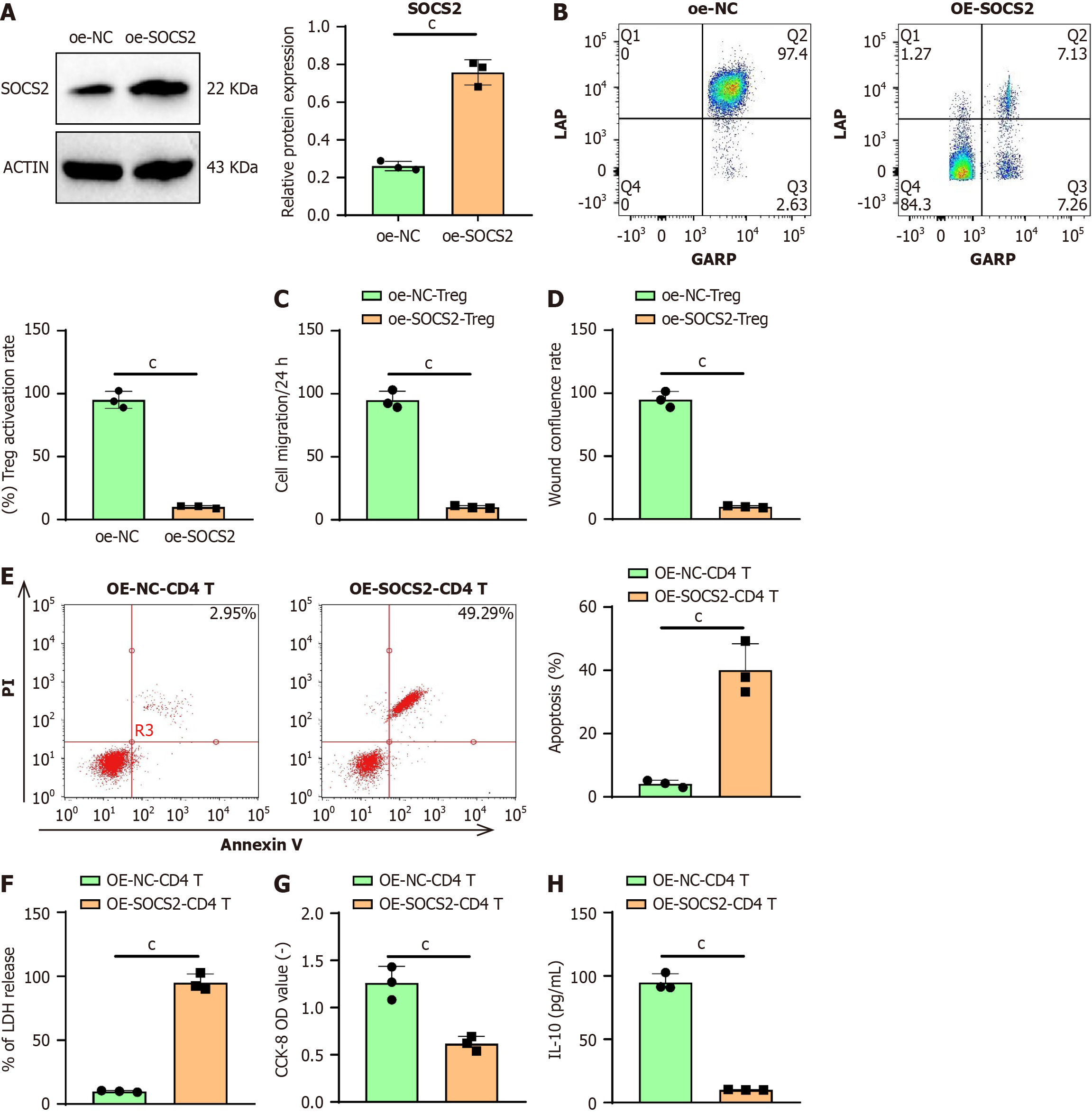
Figure 5 Suppression of regulatory T-cell cell activity by suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 inhibits the growth of liver hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Quantification of suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 protein expression in CD4 T cells by Western blotting; B: Flow cytometry analysis of the activation of CD4 T cells; C: Representative images and cell numbers of Huh-7 migration assessed by Transwell assay; D: Scratch assay to detect representative images of Huh-7 and wound closure rate, where the wound closure rate% = (a - b) × 100%; E: Flow cytometry measuring apoptosis rate of Huh-7 cells after co-culture treatment; F: Measurement of LDH release in Huh-7 cells after co-culture treatment; G: Assessment of Huh-7 cell viability after co-culture treatment using CCK-8 assay; H: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay quantifying the expression level of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in Huh-7 cells after co-culture treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SD (with cell experiments repeated thrice, cP < 0.001, analyzed using t-test). SOCS2: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2; Treg: Regulatory T-cell; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; PI: Propidium iodide.
- Citation: Lan X, Zhang H, Chen ZY, Wang J, Zhang SC, Li Q, Ke JY, Wei W, Huang R, Tang X, Chen SP, Huang TT, Zhou YW. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 modulates regulatory T cell activity to suppress liver hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(13): 100566
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i13/100566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i13.100566