Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2025; 31(12): 100855
Published online Mar 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.100855
Published online Mar 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.100855
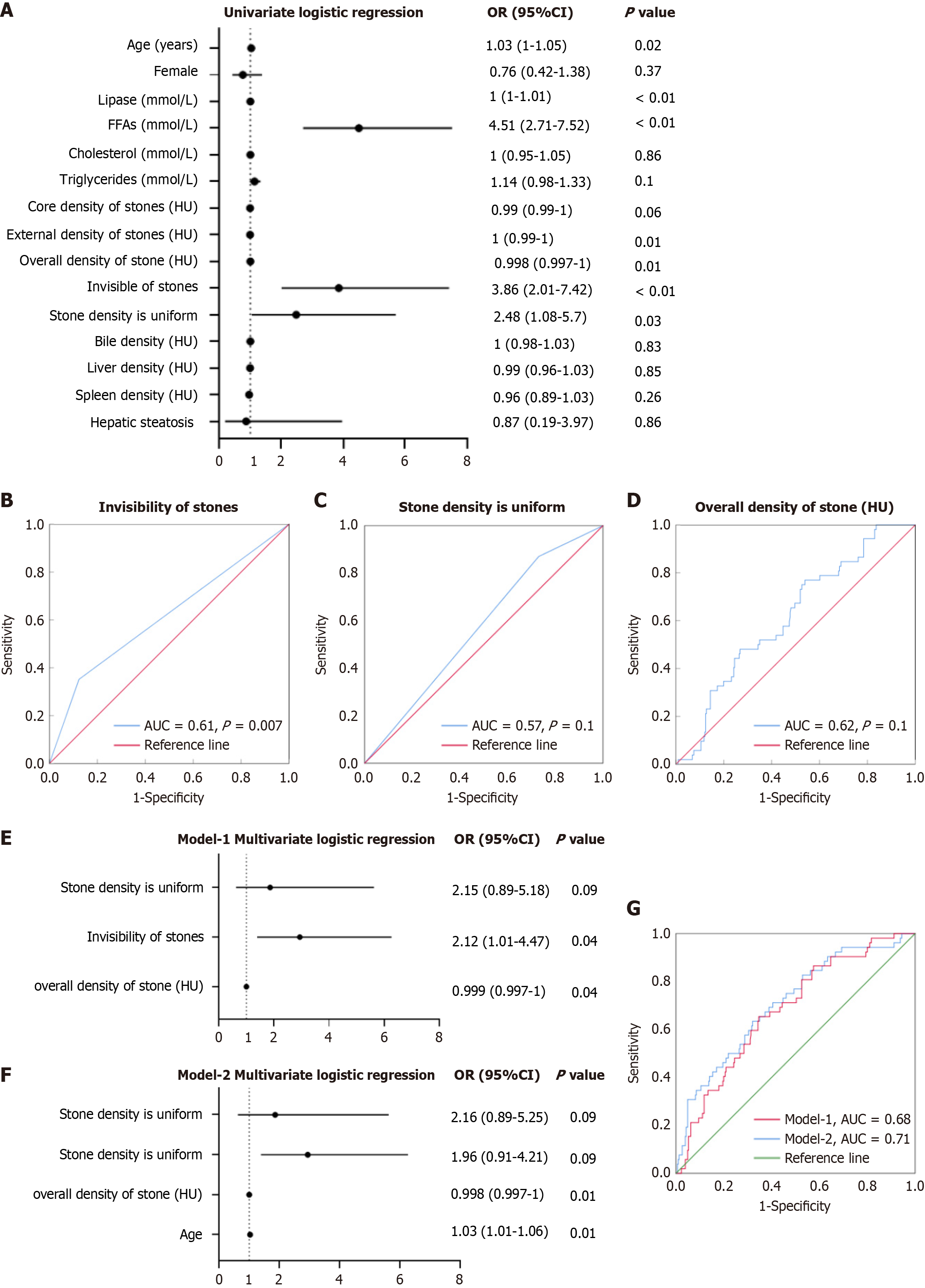
Figure 5 Predictive value of computed tomography imaging parameters for diagnosing occult pancreaticobiliary reflux.
A: Forest plot of univariate logistic regression analysis for occult pancreaticobiliary reflux (OPBR), showing the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for various clinical and imaging parameters; B: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve evaluating the diagnostic performance of CT invisible stones for OPBR; C: ROC curve assessing the predictive ability of uniform stones in diagnosing OPBR; D: ROC curve illustrating the predictive value of overall stone density for OPBR detection; E: Multivariate logistic regression (Model-1) incorporating stone invisibility, stone density uniformity and overall stone density; F: Multivariate logistic regression (Model-2) including age as an additional factor. The overall predictive accuracy improved; G: ROC curves comparing the diagnostic performance of Model-1 and Model-2, demonstrating the enhanced predictive value when age was included. AUC: Area under the curve; FFA: Free fatty acid.
- Citation: Qiu C, Xiang YK, Hu H, Da XB, Li G, Zhang YY, Zhang HL, Zhang C, Yang YL. Characterization of gallbladder stones associated with occult pancreaticobiliary reflux using computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(12): 100855
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i12/100855.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.100855