Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 98974
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.98974
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.98974
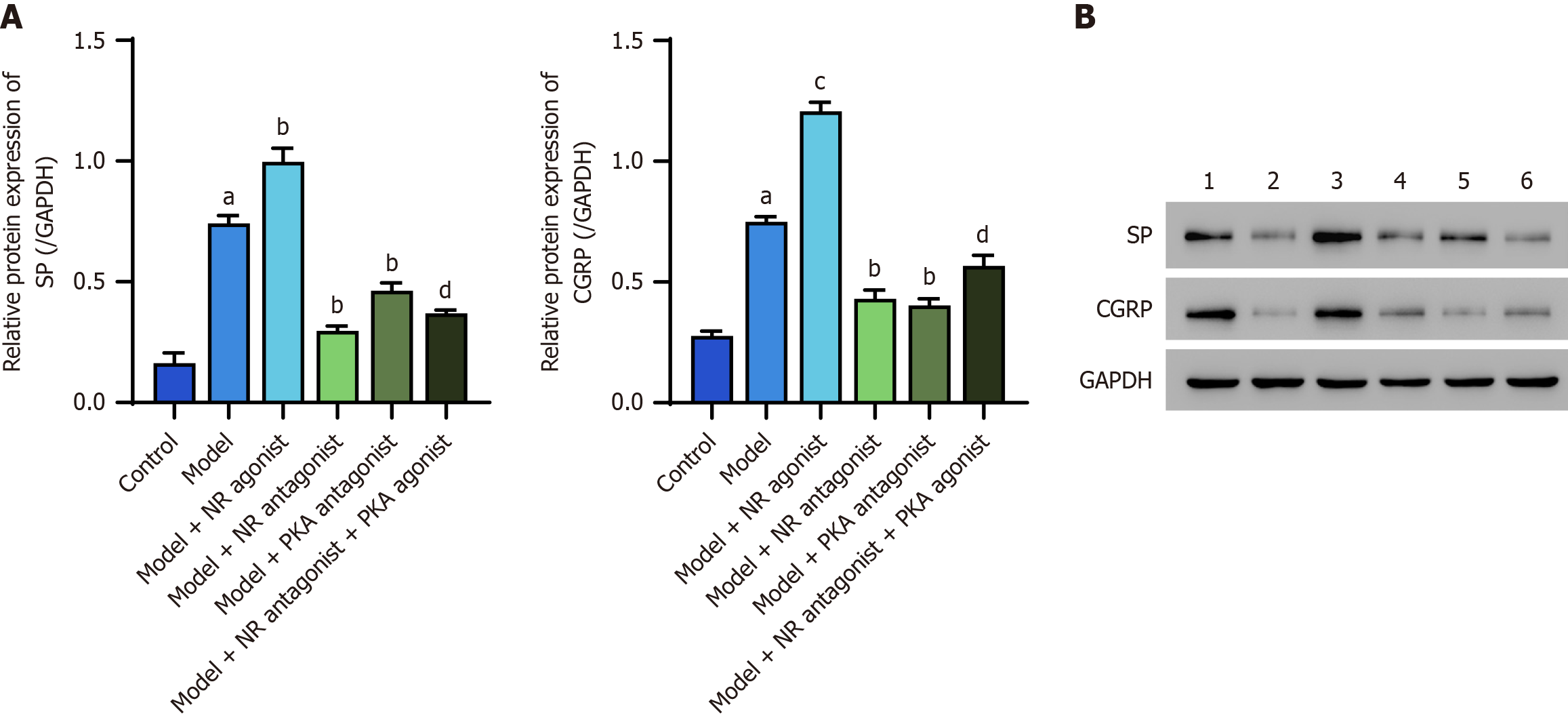
Figure 8 Results of Western blot of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the distal esophageal mucosa of rats in each group.
A: Relative expression of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the distal esophageal mucosa among different groups of rats. Data are presented as mean ± SD; B: Relative expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) pathway proteins in the distal esophageal mucosa of rats in each group [1: Model; 2: Control; 3: Model + NMDA receptor (NMDAR) agonist; 4: Model + NMDAR antagonist; 5: Model + protein kinase A (PKA) antagonist; 6: Model + NMDAR antagonist + PKA agonist]. aP < 0.001, model group vs control group. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, model + NR agonist group, model + NR antagonist group, model + PKA antagonist group vs model group. dP < 0.01, model + NR antagonist + PKA agonist group vs model + NR antagonist group. NR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; PKA: Protein kinase A; SP: Substance P; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide.
- Citation: Wang Y, Li GW, Zhu SL, Xu TT, Qin YW, Cheng CQ, Zheng QW, He C, Zhou BD, Fang SQ. NMDAR2B/PKA/CREB signaling pathway contributes to esophageal neuropathic pain in gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 98974
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/98974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.98974