Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 103449
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.103449
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.103449
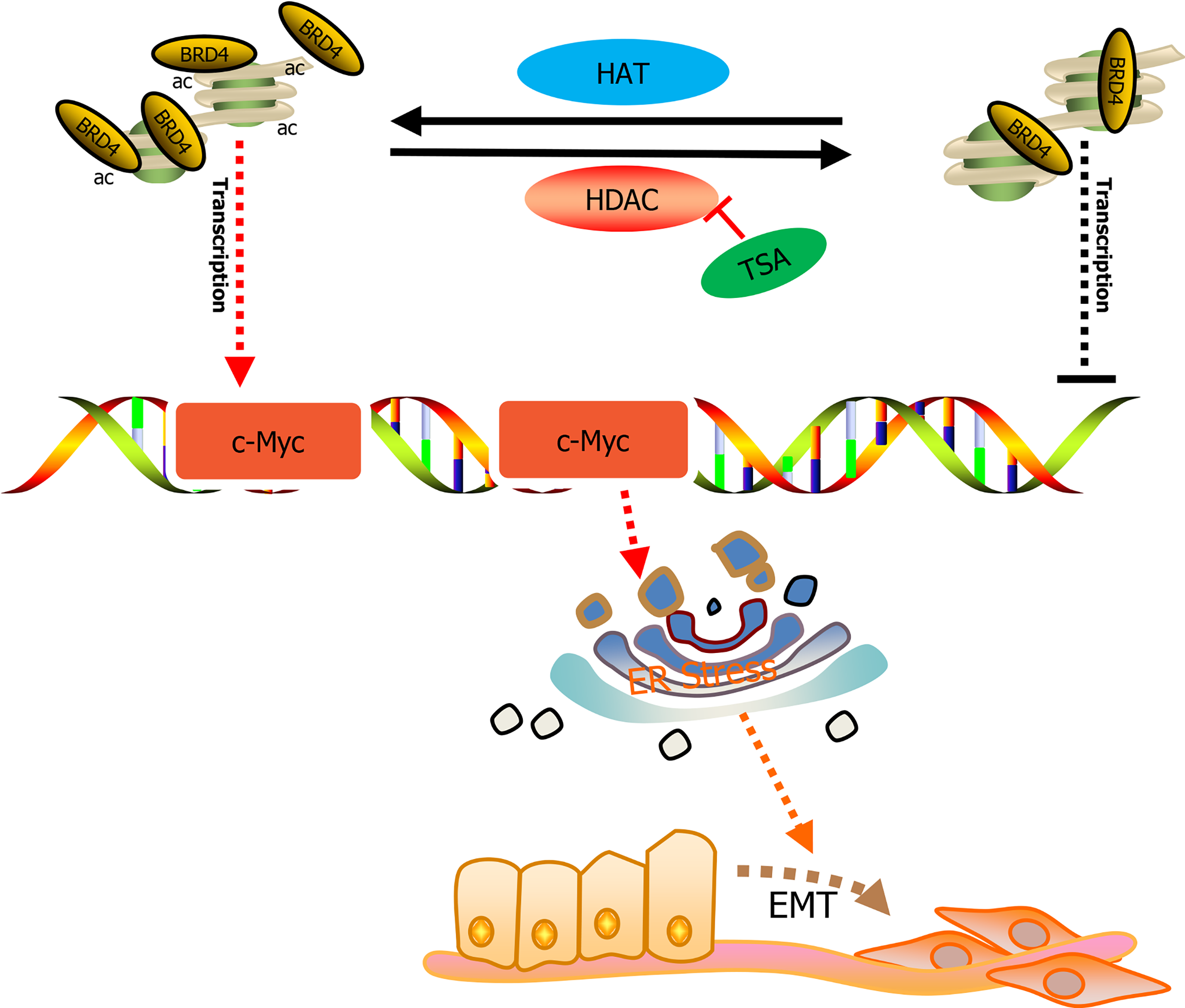
Figure 7 A proposed model illustrating the mechanism by which trichostatin A promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration.
ac: Acetylation; TSA: Trichostatin A; HAT: Histone lysine acetyltransferase; HDAC: Histone deacetylases; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; c-Myc: Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene.
- Citation: Chen YM, Yang WQ, Fan YY, Chen Z, Liu YZ, Zhao BS. Trichostatin A augments cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through BRD4/c-Myc endoplasmic reticulum-stress pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 103449
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/103449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.103449