Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
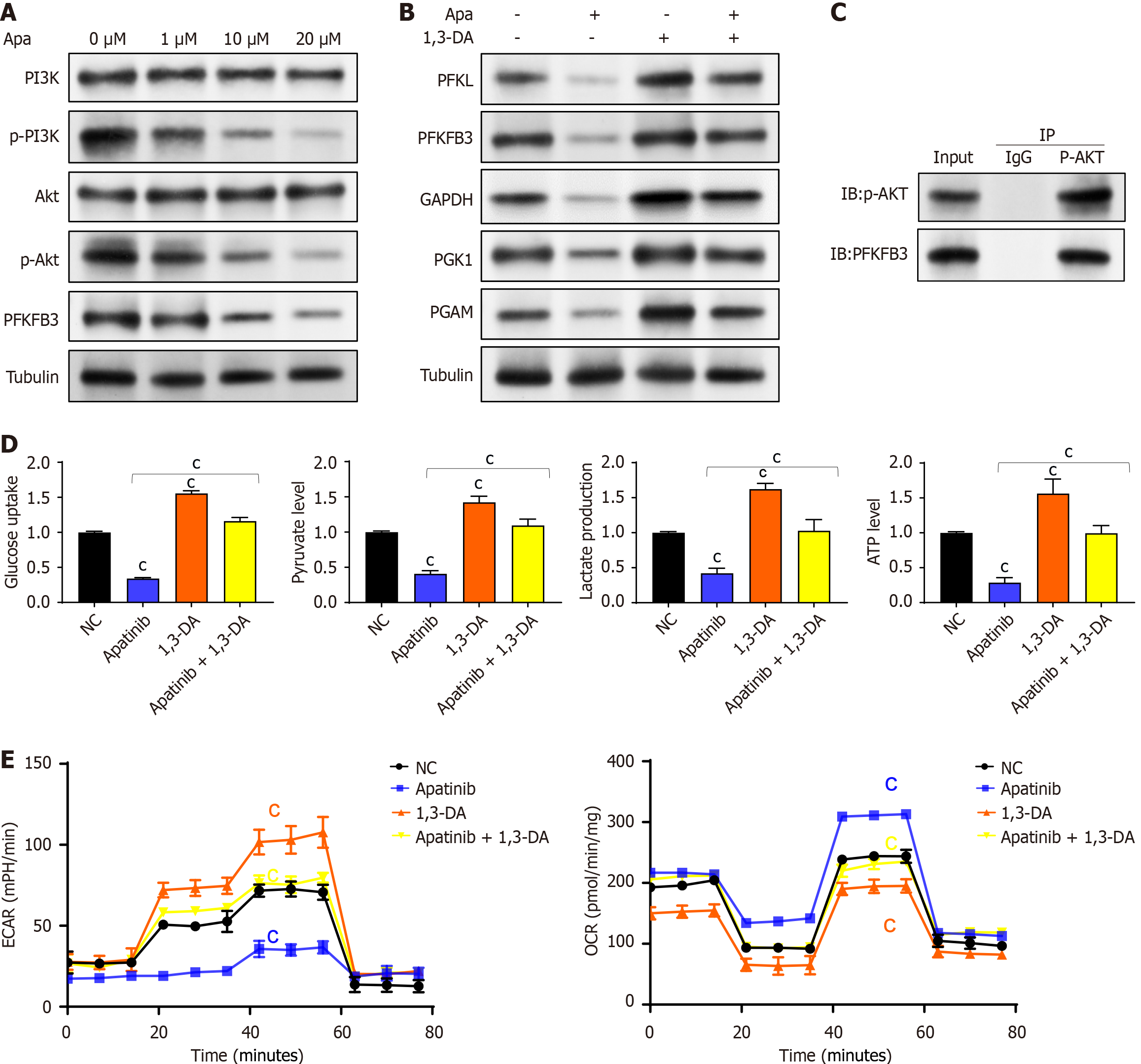
Figure 6 Apatinib inhibits glycolysis in vascular endothelial cells through regulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway.
A: Apatinib decreases the expression of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 and the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT, without affecting the total protein levels; B: The inhibition of the glycolytic pathway in vascular endothelial cells (VECs) by apatinib can be counteracted by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activator 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid; C: Coimmunoprecipitation results showed that zero acidified AKT could interact with 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; D: The effects of apatinib on glucose uptake, pyruvate generation, lactate production, and adenosine triphosphate generation during glycolysis in VECs can be reversed by 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid; E: The effects of apatinib on extracellular acidification rate and oxygen consumption rate in VECs can be reversed by 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid. cP < 0.001. Apa: Apatinib; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PFKFB3: 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; DA: Dicaffeoylquinic acid; PFKL: Phosphofructokinase liver type; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGK1: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PGAM: Phosphoglycerate mutase; IP: Immunoprecipitation; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
- Citation: Wu Y, Xie BB, Zhang BL, Zhuang QX, Liu SW, Pan HM. Apatinib regulates the glycolysis of vascular endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 102848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/102848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848