Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
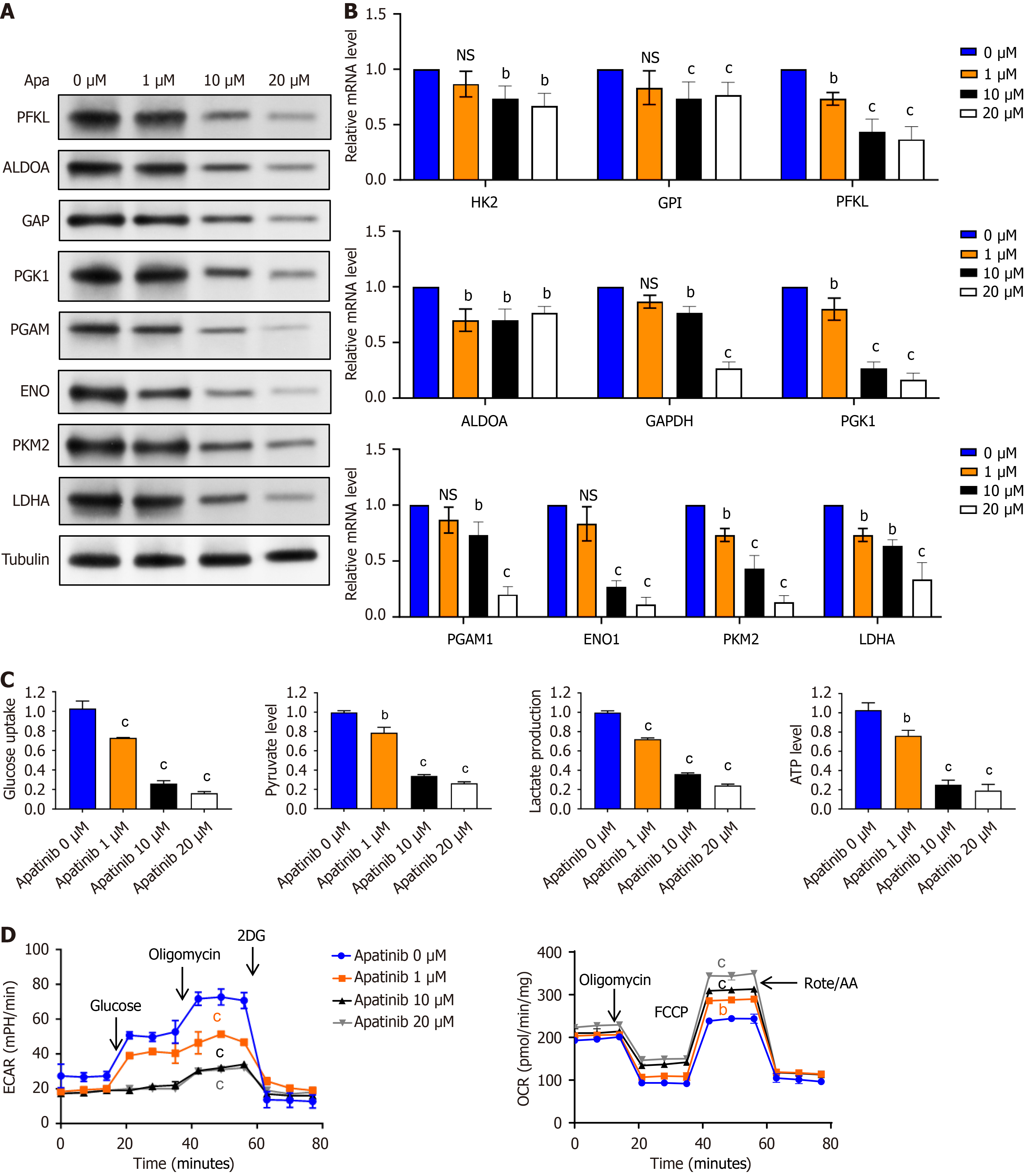
Figure 3 Apatinib suppresses glycolytic activity in vascular endothelial cells.
A: Investigation of the effects of varying concentrations of apatinib on the expression levels of key glycolytic enzymes in vascular endothelial cells (VECs) using Western blotting; B: Evaluation of the impact of different concentrations of apatinib on the expression levels of key glycolytic enzymes in VECs through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C: Assessment of the impact of different concentrations of apatinib on glucose uptake, pyruvate generation, lactate production, and adenosine triphosphate generation during glycolysis in VECs; D: Examination of the impact of varying apatinib concentrations on extracellular acidification rate and oxygen consumption rate in VECs. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Apa: Apatinib; PFKL: Phosphofructokinase liver type; ALDOA: Aldolase A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGK1: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PGAM: Phosphoglycerate mutase; ENO: Enolase; PKM2: Pyruvate kinase M2; LDHA: Lactate dehydrogenase A; NS: Not significant; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; ECAR: Extracellular acidification rate; OCR: Oxygen consumption rate.
- Citation: Wu Y, Xie BB, Zhang BL, Zhuang QX, Liu SW, Pan HM. Apatinib regulates the glycolysis of vascular endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 102848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/102848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848