Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2025; 31(10): 103133
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133
Published online Mar 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133
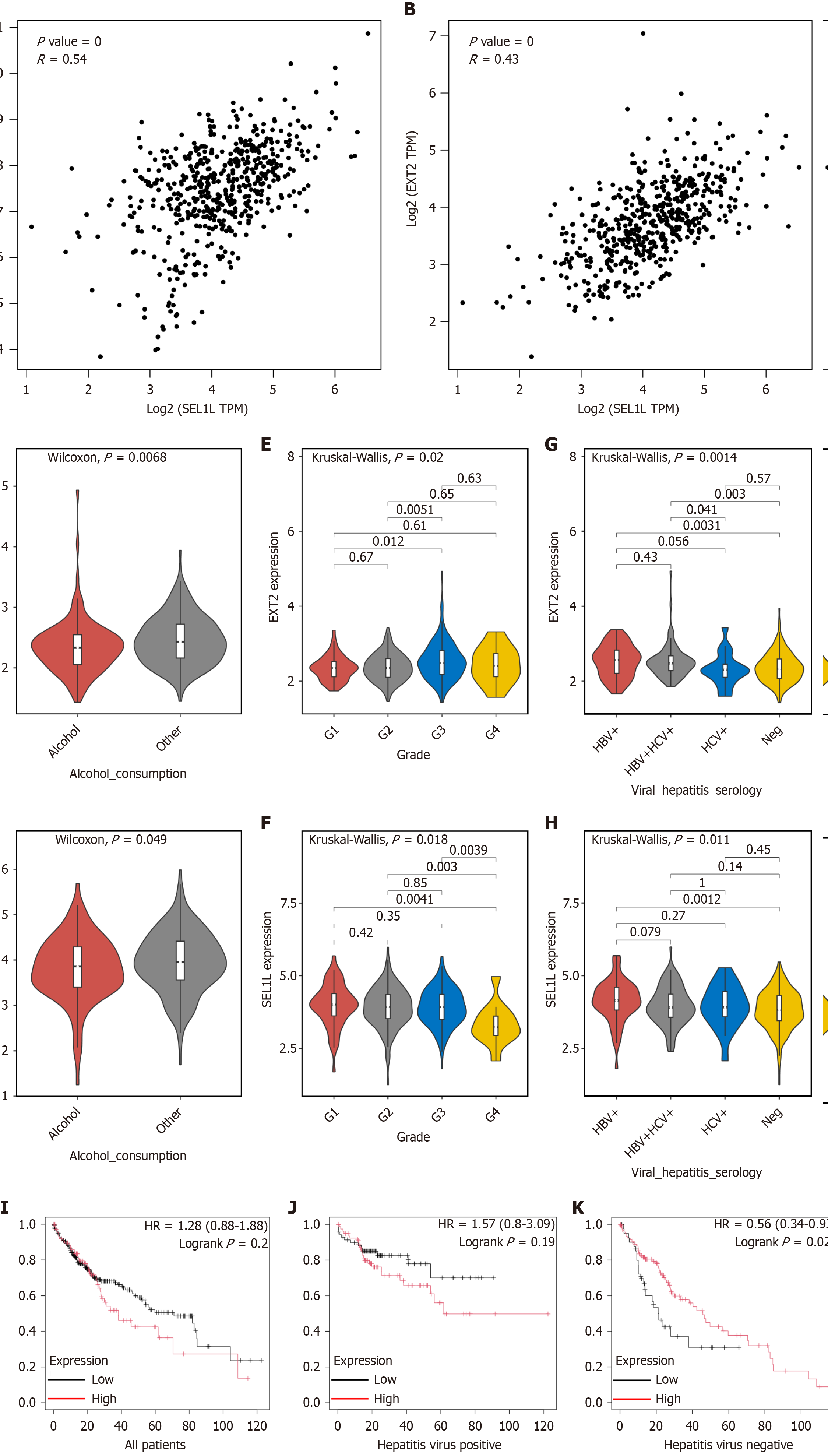
Figure 7 The expression of EXT2 in human tissue and the survival analysis.
A: Correlation analysis of EXT2 and SEL1L in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) and liver tissues performed by GEPIA2; B: Correlation analysis of heavy-chain binding protein and SEL1L in LIHC and liver tissues performed by GEPIA2; The expression of EXT2 and SEL1L in patients in different subgroups were compared based on clinical factors such as C and D: Alcohol consumption; E and F: Neoplasm histologic grade; G and H: Hepatitis virus infection; I: Survival analysis of EXT2 in all patients; J and K: Survival analysis of EXT2 in patients with/without hepatitis virus infection. TPM: Transcripts per million; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HR: Hazard ratio.
- Citation: Chen JN, Wang L, He YX, Sun XW, Cheng LJ, Li YN, Yoshida S, Shen ZY. SEL1L-mediated endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation inhibition suppresses proliferation and migration in Huh7 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(10): 103133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i10/103133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.103133